Whole exome sequencing of FFPE samples-expanding the horizon of forensic molecular autopsies
- PMID: 36346469
- PMCID: PMC10247852
- DOI: 10.1007/s00414-022-02906-x
Whole exome sequencing of FFPE samples-expanding the horizon of forensic molecular autopsies
Abstract
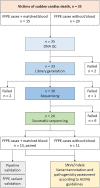
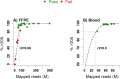
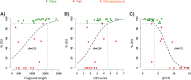
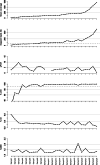
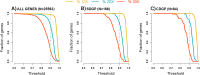
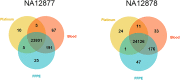
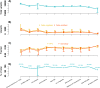
Forensic molecular autopsies have emerged as a tool for medical examiners to establish the cause of death. It is particularly useful in sudden unexplained deaths where the cause of death cannot be determined with a regular medical autopsy. We provide the first study of exome data from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples (FFPE) paired with data from high-quality blood samples in forensic applications. The approach allows exploration of the potential to use FFPE samples for molecular autopsies and identify variants in extensive exome data. We leverage the high uniformity of the hybridization capture approach provided by Twist Bioscience to target the complete exome and sequence the libraries on a NextSeq 550. Our findings suggest that exome sequencing is feasible for 24 out of a total of 35 included FFPE samples. When successful, the coverage across the exome is comparatively high (> 90% covered to 20X) and uniform (fold80 below 1.5). Detailed variant comparisons for matched FFPE and blood samples show high concordance with few false variants (positive predictive value of 0.98 and a sensitivity of 0.97) with no distinct FFPE artefacts. Ultimately, we apply carefully constructed forensic gene panels in a stepwise manner to find genetic variants associated with the clinical phenotype and with relevance to the sudden unexplained death.
Keywords: Arrhythmia; Cardiomyopathy; FFPE; Molecular autopsy; SCD; WES.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Stiles MK, Wilde AAM, Abrams DJ, Ackerman MJ, Albert CM, Behr ER, et al. 2020 APHRS/HRS expert consensus statement on the investigation of decedents with sudden unexplained death and patients with sudden cardiac arrest, and of their families. Heart Rhythm. 2021;18(1):e1–e50. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2020.10.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

