Potential usefulness of Mediterranean diet polyphenols against COVID-19-induced inflammation: a review of the current knowledge
- PMID: 36346507
- PMCID: PMC9641689
- DOI: 10.1007/s13105-022-00926-0
Potential usefulness of Mediterranean diet polyphenols against COVID-19-induced inflammation: a review of the current knowledge
Abstract
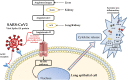
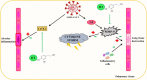
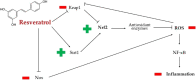
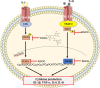
The Mediterranean diet is a dietary pattern typical of the populations living in the Mediterranean basin during the 50s-60s of the last century. This diet has demonstrated beneficial effects in the prevention of several pathologies such as cardiovascular diseases, metabolic syndrome, or several cancer types, at least in part, due to its antioxidant compounds. Since the COVID-19 pandemic started, different authors have been studying the effects of certain dietary habits on the presence of COVID-19 and its severity, and the Mediterranean diet is one of them. This review gathers data from studies supporting the potential usefulness of the main phenolic compounds present in the Mediterranean diet, based on their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, as preventive/therapeutic agents against COVID-19. The current evidence supports the potential benefits that hydroxytyrosol, resveratrol, flavonols such as quercetin, flavanols like catechins, and flavanones on the order of naringenin could have on COVID-19. This is due to the increase in the synthesis and translocations of Nrf-2, which increases the activity of antioxidant enzymes and thus reduces ROS production, the scavenging of free radicals, and the suppression of the activity of MMP-9, which is involved in the cytokine storm, and the inhibition of NF-κB.
Keywords: Antioxidants; COVID-19; Mediterranean diet; Polyphenols.
© 2022. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to University of Navarra.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Polyphenols Contained in Mediterranean Diet in Obesity: Molecular Mechanisms.Molecules. 2021 Feb 12;26(4):985. doi: 10.3390/molecules26040985. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33673390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mediterranean diet polyphenols reduce inflammatory angiogenesis through MMP-9 and COX-2 inhibition in human vascular endothelial cells: a potentially protective mechanism in atherosclerotic vascular disease and cancer.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012 Nov 15;527(2):81-9. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2012.05.003. Epub 2012 May 14. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012. PMID: 22595400
-
Effects of the Mediterranean diet polyphenols on cancer development.J Prev Med Hyg. 2022 Oct 17;63(2 Suppl 3):E74-E80. doi: 10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2022.63.2S3.2749. eCollection 2022 Jun. J Prev Med Hyg. 2022. PMID: 36479482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular effects of the Mediterranean diet-part II: role of omega-3 fatty acids and olive oil polyphenols.Vascul Pharmacol. 2014 Dec;63(3):127-34. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2014.07.001. Epub 2014 Oct 16. Vascul Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25446163 Review.
-
Polyphenols of the Mediterranean Diet and Their Metabolites in the Prevention of Colorectal Cancer.Molecules. 2021 Jun 8;26(12):3483. doi: 10.3390/molecules26123483. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34201125 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: The Influence of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Mitochondrial Dysfunctions, and the Role of Polyphenols.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Oct 10;17(10):1354. doi: 10.3390/ph17101354. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mediterranean Diet Influence on SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Adverse Reaction: Friend or Foe?Nutrients. 2024 Jun 12;16(12):1846. doi: 10.3390/nu16121846. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38931201 Free PMC article.
-
Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective.Life (Basel). 2025 Jan 16;15(1):113. doi: 10.3390/life15010113. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39860053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Polyphenols Derived from the European Olive Tree, Olea europaea L., in Long COVID and Other Conditions Involving Cognitive Impairment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 14;25(20):11040. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011040. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nobiletin and Eriodictyol Suppress Release of IL-1β, CXCL8, IL-6, and MMP-9 from LPS, SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein, and Ochratoxin A-Stimulated Human Microglia.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 14;26(2):636. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020636. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859348 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alkhatib A. Olive oil nutraceuticals and chronic disease prevention: more than an offshoot of the Mediterranean diet. In: Preedy VR, Watson RR, editors. The Mediterranean Diet. 2. London: Academic Press; 2020. pp. 363–370.
-
- Bousquet J, Cristol JP, Czarlewski W, Anto JM, Martineau A, Haahtela T, Fonseca SC, Iaccarino G, Blain H, Fiocchi A, Canonica GW, Fonseca JA, Vidal A, Choi HJ, Kim HJ, Le Moing V, Reynes J, Sheikh A, Akdis CA, Zuberbier T, ARIA groupl Nrf2-interacting nutrients and COVID-19: time for research to develop adaptation strategies. Clin Transl Allergy. 2020;10:58. doi: 10.1186/s13601-020-00362-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

