The effect of plasma transfusion in an experimental two-hit animal model of transfusion-associated circulatory overload with heart failure
- PMID: 36346876
- PMCID: PMC10159801
- DOI: 10.2450/2022.0141-22
The effect of plasma transfusion in an experimental two-hit animal model of transfusion-associated circulatory overload with heart failure
Abstract
Background: Transfusion-associated circulatory overload (TACO) is a leading cause of transfusion-related morbidity and mortality. TACO follows a two-hit pathophysiology, where comorbidities like cardiac or renal failure act as the first hit followed by blood transfusion as a second hit. Observational studies suggest that plasma transfusion is more likely to cause TACO than other blood products. We conducted a randomized animal study to gather evidence that plasma transfusion can induce TACO.
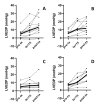
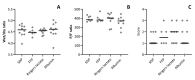
Material and methods: As a first hit a large myocardial infarction was created in male Wistar rats. Then animals were randomized to receive 4 units of solvent/ detergent-treated pooled plasma (SDP), fresh frozen plasma (FFP), a colloid control (albumin 5%) or a crystalloid fluid control (Ringer's lactate) (n=10 per group). The primary outcome was the difference between pre- and post-transfusion left-ventricular end diastolic pressure (ΔLVEDP). Secondary outcomes were markers for acute lung injury; lung wet/dry weight ratio, PaO2/FiO2 ratio and pulmonary histological assessment.
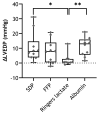
Results: Pre-transfusion characteristics were similar between groups. ΔLVEDP increased significantly after transfusion with SDP (7.7 mmHg; 4.5-10.5) and albumin (13.0 mmHg; 6.5-15.2), but not after FFP (7.9 mmHg, 1.1; 11.3) compared to infusion with Ringer's lactate (0.6 mmHg; 0.4-2.2), p=0.007, p=0.0005 and p=0.14 respectively. There were no significant differences in ΔLVEDP between groups receiving SDP, FFP or albumin. There was no increase in acute lung injury in any group compared to other groups.
Discussion: Circulatory overload, measured as ΔLVEDP, was induced after transfusion of SDP or albumin, but not after infusion of Ringer's lactate. These results show that the effect of plasma transfusion on ΔLVEDP differs from fluid overload induced by crystalloid infusion. Colloid osmotic pressure may be an important component in the development of TACO and should be a target for future research.
Conflict of interest statement
A.P.J. Vlaar received a Landsteiner Foundation for Blood Research (LSBR) fellowship grant, number 1931F as is stated under funding and resources. All other Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Comment in
-
Acute myocardial infarction and blood transfusion: lessons learned from animal models and clinical studies.Blood Transfus. 2023 May;21(3):185-188. doi: 10.2450/BloodTransfus.427. Blood Transfus. 2023. PMID: 37141620 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lieberman L, Maskens C, Cserti-Gazdewich C, Hansen M, Lin Y, Pendergrast J, et al. A retrospective review of patient factors, transfusion practices, and outcomes in patients with transfusion-associated circulatory overload. Transfus Med Rev. 2013;27:206–218. doi: 10.1016/j.tmrv.2013.07.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bolton-Maggs PHB, Poles D, et al., editors. on behalf of the Serious Hazards of Transfusion (SHOT) Steering Group. The 2017 Annual SHOT Report. 2018
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
