Genome-Wide Screen for Enhanced Noncanonical Amino Acid Incorporation in Yeast
- PMID: 36346914
- PMCID: PMC10065164
- DOI: 10.1021/acssynbio.2c00267
Genome-Wide Screen for Enhanced Noncanonical Amino Acid Incorporation in Yeast
Abstract
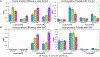
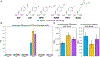
Numerous applications of noncanonical amino acids (ncAAs) in basic biology and therapeutic development require efficient protein biosynthesis using an expanded genetic code. However, achieving such incorporation at repurposed stop codons in cells is generally inefficient and limited by complex cellular processes that preserve the fidelity of protein synthesis. A more comprehensive understanding of the processes that contribute to ncAA incorporation would aid in the development of genomic engineering strategies for augmenting genetic code manipulation. In this work, we used a series of fluorescent reporters to screen a pooled Saccharomyces cerevisiae molecular barcoded yeast knockout (YKO) collection. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting enabled isolation of strains encoding single-gene deletions exhibiting improved ncAA incorporation efficiency in response to the amber (TAG) stop codon; 55 unique candidate deletions were identified. The deleted genes encoded for proteins that participate in diverse cellular processes, including many genes that have no known connection with protein translation. We then verified that two knockouts, yil014c-aΔ and alo1Δ, exhibited improved ncAA incorporation efficiency starting from independently acquired strains possessing the knockouts. Using additional orthogonal translation systems and ncAAs, we determined that yil014c-aΔ and alo1Δ enhance ncAA incorporation efficiency without loss of fidelity over a wide range of conditions. Our findings highlight opportunities for further modulating gene expression with genetic, genomic, and synthetic biology approaches to improve ncAA incorporation efficiency. In addition, these discoveries have the potential to enhance our fundamental understanding of protein translation. Ultimately, cells that efficiently biosynthesize ncAA-containing proteins will streamline the realization of applications utilizing expanded genetic codes ranging from basic biology to drug discovery.
Keywords: amber suppression; aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases; fluorescence-activated cell sorting; noncanonical amino acids; yeast knockout collection.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
Tufts University has submitted a patent application for the aaRS sequence of SpecOPGRS-3: U.S. Patent Application No. PCT/US22/29775.
Figures
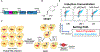
Similar articles
-
High-Throughput Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase Engineering for Genetic Code Expansion in Yeast.ACS Synth Biol. 2022 Jul 15;11(7):2284-2299. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.1c00626. Epub 2022 Jul 6. ACS Synth Biol. 2022. PMID: 35793554 Free PMC article.
-
A Robust and Quantitative Reporter System To Evaluate Noncanonical Amino Acid Incorporation in Yeast.ACS Synth Biol. 2018 Sep 21;7(9):2256-2269. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.8b00260. Epub 2018 Sep 4. ACS Synth Biol. 2018. PMID: 30139255 Free PMC article.
-
Broadening the Toolkit for Quantitatively Evaluating Noncanonical Amino Acid Incorporation in Yeast.ACS Synth Biol. 2021 Nov 19;10(11):3094-3104. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.1c00370. Epub 2021 Nov 3. ACS Synth Biol. 2021. PMID: 34730946 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering the Genetic Code in Cells and Animals: Biological Considerations and Impacts.Acc Chem Res. 2017 Nov 21;50(11):2767-2775. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00376. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Acc Chem Res. 2017. PMID: 28984438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Not-so-popular" orthogonal pairs in genetic code expansion.Protein Sci. 2023 Feb;32(2):e4559. doi: 10.1002/pro.4559. Protein Sci. 2023. PMID: 36585833 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution and synthetic biology.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2023 Dec;76:102394. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2023.102394. Epub 2023 Oct 4. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37801925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncanonical Amino Acids in Biocatalysis.Chem Rev. 2024 Jul 24;124(14):8740-8786. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00120. Epub 2024 Jul 3. Chem Rev. 2024. PMID: 38959423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Screen for Enhanced Noncanonical Amino Acid Incorporation in Yeast.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2760:219-251. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3658-9_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38468092
-
Reaching New Heights in Genetic Code Manipulation with High Throughput Screening.Chem Rev. 2024 Nov 13;124(21):12145-12175. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00329. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Chem Rev. 2024. PMID: 39418482 Review.
-
Protein Engineering and High-Throughput Screening by Yeast Surface Display: Survey of Current Methods.Small Sci. 2023 Dec;3(12):2300095. doi: 10.1002/smsc.202300095. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Small Sci. 2023. PMID: 39071103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chin JW, Expanding and reprogramming the genetic code. Nature 2017, 550 (7674), 53–60. - PubMed
-
- Wang L; Xie J; Schultz PG, Expanding the genetic code. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 2006, 35, 225–49. - PubMed
-
- Liu CC; Schultz PG, Adding new chemistries to the genetic code. Annu Rev Biochem 2010, 79, 413–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

