New Paradigm for Nano-Bio Interactions: Multimolecular Assembly of a Prototypical Disordered Protein with Ultrasmall Nanoparticles
- PMID: 36346924
- PMCID: PMC9706667
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c02902
New Paradigm for Nano-Bio Interactions: Multimolecular Assembly of a Prototypical Disordered Protein with Ultrasmall Nanoparticles
Abstract
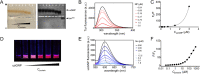
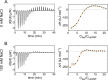
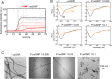
Understanding the interactions between nanoparticles (NPs) and proteins is crucial for the successful application of NPs in biological contexts. Protein adsorption is dependent on particle size, and protein binding to ultrasmall (1-3 nm) NPs is considered to be generally weak. However, most studies have involved structured biomacromolecules, while the interactions of ultrasmall NPs with intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) have remained elusive. IDPs are abundant in eukaryotes and found to associate with NPs intracellularly. As a model system, we focused on ultrasmall gold nanoparticles (usGNPs) and tau, a cytosolic IDP associated with Alzheimer's disease. Using site-resolved NMR, steady-state fluorescence, calorimetry, and circular dichroism, we reveal that tau and usGNPs form stable multimolecular assemblies, representing a new type of nano-bio interaction. Specifically, the observed interaction hot spots explain the influence of usGNPs on tau conformational transitions, with implications for the intracellular targeting of aberrant IDP aggregation.
Keywords: NMR spectroscopy; intrinsically disordered proteins; protein aggregation; protein−nanoparticle interaction; ultrasmall nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Cedervall T.; Lynch I.; Lindman S.; Berggard T.; Thulin E.; Nilsson H.; Dawson K. A.; Linse S. Understanding the Nanoparticle-Protein Corona Using Methods to Quantify Exchange Rates and Affinities of Proteins for Nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 2050–2055. 10.1073/pnas.0608582104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

