Reduced CV risk with long-term GH replacement in AGHD: data from two large observational studies
- PMID: 36347049
- PMCID: PMC9782424
- DOI: 10.1530/EC-22-0267
Reduced CV risk with long-term GH replacement in AGHD: data from two large observational studies
Abstract
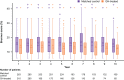
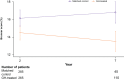
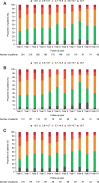
Adult growth hormone deficiency (AGHD) is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular (CV) disease. Long-term growth hormone (GH) treatment could improve CV outcomes. The objective of this study was to evaluate CV disease risk in patients with AGHD who received GH replacement therapy for up to 10 years as part of NordiNet® IOS (NCT00960128) and the ANSWER Program (NCT01009905). The studies were observational, non-interventional and multicentre, monitoring long-term effectiveness and safety of GH treatment. NordiNet® IOS involved 23 countries (469 sites) across Europe and the Middle East. The ANSWER Program was conducted in the USA (207 sites). This analysis included patients aged 18-75 years who were GH naïve at study entry, who had ≤10 years of GH treatment data and who could be assessed for CV risk for at least 1 follow-up year. The main outcome measure was risk of CV disease by age 75 years, as calculated with the Multinational Cardiovascular Risk Consortium model (Brunner score) using non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol adjusted for age, sex and CV risk factors. The results of this analysis showed that CV risk decreased gradually over the 10-year period for GH-treated patients. The risk was lower for patients treated for 2 and 7 years vs age- and sex-matched control groups (not yet started treatment) (14.51% vs 16.15%; P = 0.0105 and 13.53% vs 16.81%; P = 0.0001, respectively). This suggests that GH treatment in people with AGHD may reduce the risk of CV disease by age 75 years compared with matched controls.
Keywords: ANSWER; NordiNet; cardiovascular risk; growth hormone; norditropin.
Conflict of interest statement
CH has received honoraria for lectures and consultation from Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Ascendis and Sandoz and is a member of the Global Steering Committee for the PATRO Adults study. BMKB has been the principal investigator of a research grant from Ascendis to Massachusetts General Hospital and has received occasional consulting honoraria from Ascendis, Merck-Serono and Novo Nordisk. JMF is a consultant for Novo Nordisk. MBG has received research support from Chiasma, Corcept, Crinetics, Ipsen, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Recordati and Strongbridge and has received honoraria for consultation from HRA Pharma, Ipsen, Novo Nordisk and Recordati. AHO is an employee of and stockholder in Novo Nordisk. NK is an employee of Novo Nordisk and a stockholder in Novo Nordisk and Pfizer. NN is an employee of Novo Nordisk. MW has received consulting and speaker honoraria from Ipsen, Lilly, Recordati and Novo Nordisk.
Figures


References
-
- Amato G, Carella C, Fazio S, La Montagna G, Cittadini A, Sabatini D, Marciano-Mone C, Sacca L, Bellastella A. Body composition, bone metabolism, and heart structure and function in growth hormone (GH)-deficient adults before and after GH replacement therapy at low doses. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 1993771671–1676. (10.1210/jcem.77.6.8263158) - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

