Pharmacological blockade of TEAD-YAP reveals its therapeutic limitation in cancer cells
- PMID: 36347861
- PMCID: PMC9643419
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-34559-0
Pharmacological blockade of TEAD-YAP reveals its therapeutic limitation in cancer cells
Abstract
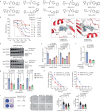
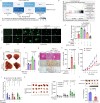
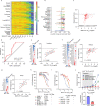
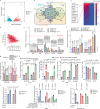
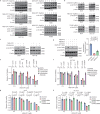
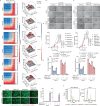
Targeting TEAD autopalmitoylation has been proposed as a therapeutic approach for YAP-dependent cancers. Here we show that TEAD palmitoylation inhibitor MGH-CP1 and analogues block cancer cell "stemness", organ overgrowth and tumor initiation in vitro and in vivo. MGH-CP1 sensitivity correlates significantly with YAP-dependency in a large panel of cancer cell lines. However, TEAD inhibition or YAP/TAZ knockdown leads to transient inhibition of cell cycle progression without inducing cell death, undermining their potential therapeutic utilities. We further reveal that TEAD inhibition or YAP/TAZ silencing leads to VGLL3-mediated transcriptional activation of SOX4/PI3K/AKT signaling axis, which contributes to cancer cell survival and confers therapeutic resistance to TEAD inhibitors. Consistently, combination of TEAD and AKT inhibitors exhibits strong synergy in inducing cancer cell death. Our work characterizes the therapeutic opportunities and limitations of TEAD palmitoylation inhibitors in cancers, and uncovers an intrinsic molecular mechanism, which confers potential therapeutic resistance.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
X.W. has a financial interest in Tasca Therapeutics, which is developing small molecule modulators of TEAD palmitoylation and transcription factors. Dr. Wu’s interests were reviewed and are managed by Mass General Hospital, and Mass General Brigham in accordance with their conflict of interest policies. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Pan D. Hippo signaling in organ size control. Genes Dev. 2007;21:886–897. - PubMed
-
- Harvey KF, Zhang X, Thomas DM. The Hippo pathway and human cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2013;13:246–257. - PubMed
-
- Huang J, Wu S, Barrera J, Matthews K, Pan D. The Hippo signaling pathway coordinately regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by inactivating Yorkie, the Drosophila Homolog of YAP. Cell. 2005;122:421–434. - PubMed
-
- Wu S, Liu Y, Zheng Y, Dong J, Pan D. The TEAD/TEF family protein Scalloped mediates transcriptional output of the Hippo growth-regulatory pathway. Dev. Cell. 2008;14:388–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

