Correlation between brain functional connectivity and neurocognitive function in patients with left frontal glioma
- PMID: 36347905
- PMCID: PMC9643499
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-22493-6
Correlation between brain functional connectivity and neurocognitive function in patients with left frontal glioma
Abstract
The association between neurocognitive function (NCF) impairment and brain cortical functional connectivity in glioma patients remains unclear. The correlations between brain oscillatory activity or functional connectivity and NCF measured by the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale full-scale intelligence quotient scores (WAIS FSIQ), the Wechsler Memory Scale-revised general memory scores (WMS-R GM), and the Western aphasia battery aphasia quotient scores (WAB AQ) were evaluated in 18 patients with left frontal glioma using resting-state electroencephalography (EEG). Current source density (CSD) and lagged phase synchronization (LPS) were analyzed using exact low-resolution electromagnetic tomography (eLORETA). Although 2 and 2 patients scored in the borderline range of WAIS FSIQ and WMS-R GM, respectively, the mean WAIS FSIQ, WMS-R GM, and WAB AQ values of all patients were within normal limits, and none had aphasia. In the correlation analysis, lower WMS-R GM was associated with a higher LPS value between the right anterior prefrontal cortex and the left superior parietal lobule in the beta1 band (13-20 Hz, R = - 0.802, P = 0.012). These findings suggest that LPS evaluated by scalp EEG is associated with memory function in patients with left frontal glioma and mild NCF disorders.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
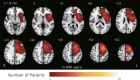
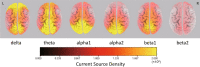
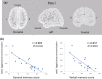
References
-
- Bello L, et al. Intraoperative subcortical language tract mapping guides surgical removal of gliomas involving speech areas. Neurosurgery. 2007;60:67–80. doi: 10.1227/01.NEU.0000249206.58601.DE. - DOI - PubMed

