A systematic study of HIF1A cofactors in hypoxic cancer cells
- PMID: 36347941
- PMCID: PMC9643333
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-23060-9
A systematic study of HIF1A cofactors in hypoxic cancer cells
Abstract
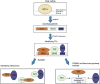
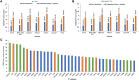
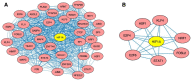
Hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF1A) is a transcription factor (TF) that forms highly structural and functional protein-protein interactions with other TFs to promote gene expression in hypoxic cancer cells. However, despite the importance of these TF-TF interactions, we still lack a comprehensive view of many of the TF cofactors involved and how they cooperate. In this study, we systematically studied HIF1A cofactors in eight cancer cell lines using the computational motif mining tool, SIOMICS, and discovered 201 potential HIF1A cofactors, which included 21 of the 29 known HIF1A cofactors in public databases. These 201 cofactors were statistically and biologically significant, with 19 of the top 37 cofactors in our study directly validated in the literature. The remaining 18 were novel cofactors. These discovered cofactors can be essential to HIF1A's regulatory functions and may lead to the discovery of new therapeutic targets in cancer treatment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Q6, a novel hypoxia-targeted drug, regulates hypoxia-inducible factor signaling via an autophagy-dependent mechanism in hepatocellular carcinoma.Autophagy. 2014 Jan;10(1):111-22. doi: 10.4161/auto.26838. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Autophagy. 2014. PMID: 24220190 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-18a inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor 1α activity and lung metastasis in basal breast cancers.Breast Cancer Res. 2014 Jul 28;16(4):R78. doi: 10.1186/bcr3693. Breast Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25069832 Free PMC article.
-
HIF1A and EPAS1 potentiate hypoxia-induced upregulation of inhibin alpha chain expression in human term cytotrophoblasts in vitro.Mol Hum Reprod. 2017 Mar 1;23(3):199-209. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gax002. Mol Hum Reprod. 2017. PMID: 28115494
-
HIF1A gene polymorphisms and human diseases: Graphical review of 97 association studies.Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2017 Jun;56(6):439-452. doi: 10.1002/gcc.22449. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28165644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia/pseudohypoxia-mediated activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in cancer.Cancer Sci. 2019 May;110(5):1510-1517. doi: 10.1111/cas.13990. Epub 2019 Mar 23. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 30844107 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia-induced cancer cell reprogramming: a review on how cancer stem cells arise.Front Oncol. 2023 Aug 8;13:1227884. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1227884. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37614497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photo-controlled co-delivery of verteporfin and acriflavine via platelets achieves potentiated glioblastoma-targeted photodynamic therapy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 May 22;23(1):371. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03395-x. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40405165 Free PMC article.
-
A survey of experimental and computational identification of small proteins.Brief Bioinform. 2024 May 23;25(4):bbae345. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae345. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39007598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha and lactate dehydrogenase-A axis in metabolic changes and aggression in esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 Mar 15;17(3):103450. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i3.103450. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40092940 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

