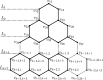
Radio antipodal number of honeycomb derived networks
- PMID: 36347943
- PMCID: PMC9643402
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-23618-7
Radio antipodal number of honeycomb derived networks
Abstract
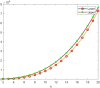
The communication in a wireless network mainly depends on the frequencies or channels assigned to them. The channels must be assigned to all the transmitters in the network without interference for effective communication. This problem is said to be a channel (frequency) assignment problem (CAP). With the limited availability of channels, CAP has become a challenging problem. This problem is modeled as a graph, where each transmitter is represented by a vertex, and two vertices are adjacent when their corresponding transmitters are close. The labelling technique in graph theory has played an important role in solving CAP, thereby the time and cost will be saved. In radio antipodal labeling, the channels were reused again for the antipodal vertices. It will reduce the usage of the number of channels, with minimum interference. Hence it is a better labeling compared to other labelings. It is a mapping [Formula: see text] from the vertex set of a graph T to the set of natural numbers such that the condition [Formula: see text], is satisfied. The span of the antipodal labeling [Formula: see text] is the maximum label allotted in a graph and is given by [Formula: see text]. The lowest value of all the spans of the antipodal labeling of graph T is said to be radio antipodal number. It is denoted by an(T). The value of the minimum span gives the bandwidth or spectrum of the channels. The honeycomb network plays an important role in communication engineering because of its structure. In this paper, the bounds of the antipodal number of honeycomb derived networks-triangular and rhombic honeycomb were obtained and represented graphically. These bounds give the optimum number of channels (bandwidth) needed for these honeycomb derived networks for effective communication without interference.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Chin, F.Y.L. Online frequency assignment in wireless communication networks, International computing and combinatorics conference. 2–2 (Springer, 2007).
-
- Orogun A, Fadeyi O, Krejcar O. Sustainable communication systems: A graph- labeling approach for cellular frequency allocation in densely populated areas. Fut. Internet. 2019;11(9):186. doi: 10.3390/fi11090186. - DOI
-
- Shah S, Abbas AW, Hussain H, Israr H. Minimizing information asymmetry interference in multi-radio multi-channel wireless mesh networks. Kuwait J. Sci. 2017;44(3):65–74.
-
- Hale WK. Frequency assignment: Theory and applications. Proc. IEEE. 1980;68(12):1497–1514. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1980.11899. - DOI
-
- Bodlaender HL, Broersma H, Fomin FV, Pyatkin AV, Woeginger GJ. Radio labeling with preassigned frequencies. SIAM J. Optim. 2004;15(1):1–16. doi: 10.1137/S1052623402410181. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous