Age alone is not a barrier to efficacy of cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy for colorectal peritoneal metastases: analysis of 1138 patients from the UK and Ireland Colorectal Peritoneal Metastases Registry
- PMID: 36347966
- PMCID: PMC9814761
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-022-02037-5
Age alone is not a barrier to efficacy of cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy for colorectal peritoneal metastases: analysis of 1138 patients from the UK and Ireland Colorectal Peritoneal Metastases Registry
Abstract
Background: The management of colorectal peritoneal metastases continues to be a challenge but recent evidence suggests cytoreductive surgery (CRS) with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) can improve survival. Uncertainty about the relationship between age and tumour biology makes patient selection challenging particularly when reported procedure related morbidity is high and impact on survival outcomes unknown. The UK and Ireland Colorectal Peritoneal Metastases Registry was reviewed to assess the influence of age on efficacy of CRS and HIPEC.
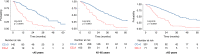
Methods: A review of outcomes from the UK and Ireland Colorectal Peritoneal Metastases Registry was performed. Data from 2000 to 2021 were included from five centres in the UK and Ireland, and the cohort were sub-divided into three age groups; <45 years, 45-65 years and >65 years old. Primarily, we examined post-operative morbidity and survival outcomes across the three age groups. In addition, we examined the impact that the completeness of cytoreduction, nodal status, or adverse pathological features had on long-term survival.
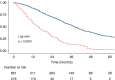
Results: During the study period, 1138 CPM patients underwent CRS HIPEC. 202 patients(17.8%) were <45 years, 549 patients(48.2%) aged 45-65 years and 387 patients(34%) >65 years. Overall, median length of surgery (CRS and HIPEC), median PCI score and rate of HIPEC administration was similar in all three groups, as was overall rates of major morbidity and/or mortality. Complete cytoreduction rates (CC0) were similar across the three cohorts; 77%, 80.6% and 81%, respectively. Median overall survival for all patients was 38 months following complete cytoreduction.
Conclusion: Age did not appear to influence morbidity or long-term survival following CRS and HIPEC. When complete cytoreduction is achieved survival outcomes are good. The addition of HIPEC can be performed safely and may reduce local recurrence within the peritoneum.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Construction and evaluation of a nomogram for predicting the prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer with peritoneal carcinomatosis treated with cytoreductive surgery plus hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023 May 25;26(5):434-441. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn441530-20230309-00071. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37217351 Chinese.
-
Outcomes of Stable Lung Colorectal Metastases on Cytoreductive Surgery and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy.J Gastrointest Surg. 2022 Aug;26(8):1724-1731. doi: 10.1007/s11605-022-05390-1. Epub 2022 Jun 29. J Gastrointest Surg. 2022. PMID: 35768716
-
[Efficacy of 1 384 cases of peritoneal carcinomatosis underwent cytoreductive surgery plus hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Mar 25;24(3):230-239. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn.441530-20201110-00603. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34645167 Chinese.
-
Cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) for colorectal and appendiceal peritoneal metastases - The Hong Kong experience and literature review.Asian J Surg. 2021 Jan;44(1):221-228. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2020.05.010. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Asian J Surg. 2021. PMID: 32605790 Review.
-
Surgical Options for Peritoneal Surface Metastases from Digestive Malignancies-A Comprehensive Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Jan 28;59(2):255. doi: 10.3390/medicina59020255. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 36837456 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A call for standardized reporting of early-onset colorectal peritoneal metastases.Eur J Cancer Prev. 2023 Nov 1;32(6):548-556. doi: 10.1097/CEJ.0000000000000816. Epub 2023 Jun 12. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 37310397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preoperative Peritoneal MRI: Usefulness to Highlight Potential Hidden Lesions for Complete Cytoreductive Surgery in Patients with Colorectal Cancer with Surgical History.Ann Surg Oncol. 2025 Aug 6. doi: 10.1245/s10434-025-18022-0. Online ahead of print. Ann Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40770528
References
-
- Dietz MV, van Kooten JP, Said I, Brandt-Kerkhof ARM, Verhoef C, Bremers AJA, et al. Survival outcomes after cytoreductive surgery with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy in patients with synchronous versus metachronous onset of peritoneal metastases of colorectal carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2022; 29:6566–76. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Franko J, Shi Q, Meyers JP, Maughan TS, Adams RA, Seymour MT, et al. Prognosis of patients with peritoneal metastatic colorectal cancer given systemic therapy: an analysis of individual patient data from prospective randomised trials from the Analysis and Research in Cancers of the Digestive System (ARCAD) database. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:1709–19. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30500-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lundy ME, Moaven O, Perry KC, Mangieri CW, Valenzuela CD, Russell GB, et al. Cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy for management of colorectal cancer with peritoneal dissemination: 30 years of experience at a single institution. J Am Coll Surg. 2022;234:546–56. doi: 10.1097/XCS.0000000000000091. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Prada-Villaverde A, Esquivel J, Lowy AM, Markman M, Chua T, Pelz J, et al. The American Society of Peritoneal Surface Malignancies evaluation of HIPEC with Mitomycin C versus Oxaliplatin in 539 patients with colon cancer undergoing a complete cytoreductive surgery. J Surg Oncol. 2014;110:779–85. doi: 10.1002/jso.23728. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous