Improved generalized ComBat methods for harmonization of radiomic features
- PMID: 36348002
- PMCID: PMC9643436
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-23328-0
Improved generalized ComBat methods for harmonization of radiomic features
Abstract
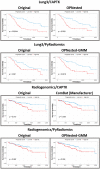
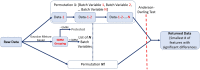
Radiomic approaches in precision medicine are promising, but variation associated with image acquisition factors can result in severe biases and low generalizability. Multicenter datasets used in these studies are often heterogeneous in multiple imaging parameters and/or have missing information, resulting in multimodal radiomic feature distributions. ComBat is a promising harmonization tool, but it only harmonizes by single/known variables and assumes standardized input data are normally distributed. We propose a procedure that sequentially harmonizes for multiple batch effects in an optimized order, called OPNested ComBat. Furthermore, we propose to address bimodality by employing a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) grouping considered as either a batch variable (OPNested + GMM) or as a protected clinical covariate (OPNested - GMM). Methods were evaluated on features extracted with CapTK and PyRadiomics from two public lung computed tomography (CT) datasets. We found that OPNested ComBat improved harmonization performance over standard ComBat. OPNested + GMM ComBat exhibited the best harmonization performance but the lowest predictive performance, while OPNested - GMM ComBat showed poorer harmonization performance, but the highest predictive performance. Our findings emphasize that improved harmonization performance is no guarantee of improved predictive performance, and that these methods show promise for superior standardization of datasets heterogeneous in multiple or unknown imaging parameters and greater generalizability.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Generalized ComBat harmonization methods for radiomic features with multi-modal distributions and multiple batch effects.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 16;12(1):4493. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-08412-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35296726 Free PMC article.
-
ComBat models for harmonization of resting-state EEG features in multisite studies.Clin Neurophysiol. 2024 Nov;167:241-253. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2024.09.019. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Clin Neurophysiol. 2024. PMID: 39369552
-
ComBat harmonization for radiomic features in independent phantom and lung cancer patient computed tomography datasets.Phys Med Biol. 2020 Jan 13;65(1):015010. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ab6177. Phys Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31835261
-
Making Radiomics More Reproducible across Scanner and Imaging Protocol Variations: A Review of Harmonization Methods.J Pers Med. 2021 Aug 27;11(9):842. doi: 10.3390/jpm11090842. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34575619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CT radiomics and PET radiomics: ready for clinical implementation?Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019 Dec;63(4):355-370. doi: 10.23736/S1824-4785.19.03192-3. Epub 2019 Sep 13. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31527578 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual adversarial deconfounding autoencoder for joint batch-effects removal from multi-center and multi-scanner radiomics data.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 1;13(1):18857. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45983-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37914758 Free PMC article.
-
Multivariate testing and effect size measures for batch effect evaluation in radiomic features.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 17;14(1):13923. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64208-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38886407 Free PMC article.
-
The Challenge of External Generalisability: Insights from the Bicentric Validation of a [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 PET Based Radiomics Signature for Primary Prostate Cancer Characterisation Using Histopathology as Reference.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Dec 7;16(23):4103. doi: 10.3390/cancers16234103. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682289 Free PMC article.
-
Resampling and harmonization for mitigation of heterogeneity in image parameters of baseline scans.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 13;12(1):21505. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26083-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36513760 Free PMC article.
-
Generative models of MRI-derived neuroimaging features and associated dataset of 18,000 samples.Sci Data. 2024 Dec 5;11(1):1330. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-04157-4. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 39638794 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haghighi, B. et al. Assessment of CT image reconstruction parameters on radiomic features in a lung cancer screening cohort: the PROSPR study. In: Medical Imaging 2020: Computer-Aided Diagnosis vol. 11314 113142G (International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2020).

