Epigenetic-Mediated Regulation of Gene Expression for Biological Control and Cancer: Cell and Tissue Structure, Function, and Phenotype
- PMID: 36348114
- PMCID: PMC9753575
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-06573-6_12
Epigenetic-Mediated Regulation of Gene Expression for Biological Control and Cancer: Cell and Tissue Structure, Function, and Phenotype
Abstract
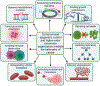
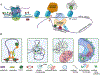
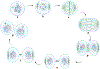
Epigenetic gene regulatory mechanisms play a central role in the biological control of cell and tissue structure, function, and phenotype. Identification of epigenetic dysregulation in cancer provides mechanistic into tumor initiation and progression and may prove valuable for a variety of clinical applications. We present an overview of epigenetically driven mechanisms that are obligatory for physiological regulation and parameters of epigenetic control that are modified in tumor cells. The interrelationship between nuclear structure and function is not mutually exclusive but synergistic. We explore concepts influencing the maintenance of chromatin structures, including phase separation, recognition signals, factors that mediate enhancer-promoter looping, and insulation and how these are altered during the cell cycle and in cancer. Understanding how these processes are altered in cancer provides a potential for advancing capabilities for the diagnosis and identification of novel therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Cell cycle control; Chromatin; Epigenetic control; Histones; Mitotic gene bookmarking; Noncoding RNAs; Nuclear structure; Nucleosomes; Spatial transcriptomics; Transcription; Tumor suppression.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Figures

References
-
- Jaenisch R and Bird A, Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: how the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nature genetics, 2003. 33(3): p. 245–254. - PubMed
-
- Osborne A, The role of epigenetics in human evolution. Bioscience Horizons: The International Journal of Student Research, 2017. 10.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

