Accurate and early prediction of the wound healing outcome of burn injuries using the wavelet Shannon entropy of terahertz time-domain waveforms
- PMID: 36348509
- PMCID: PMC9641274
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JBO.27.11.116001
Accurate and early prediction of the wound healing outcome of burn injuries using the wavelet Shannon entropy of terahertz time-domain waveforms
Abstract
Significance: Severe burn injuries cause significant hypermetabolic alterations that are highly dynamic, hard to predict, and require acute and critical care. The clinical assessments of the severity of burn injuries are highly subjective and have consistently been reported to be inaccurate. Therefore, the utilization of other imaging modalities is crucial to reaching an objective and accurate burn assessment modality.
Aim: We describe a non-invasive technique using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) and the wavelet packet Shannon entropy to automatically estimate the burn depth and predict the wound healing outcome of thermal burn injuries.
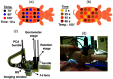
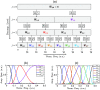
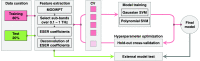
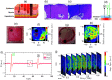
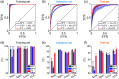
Approach: We created 40 burn injuries of different severity grades in two porcine models using scald and contact methods of infliction. We used our THz portable handheld spectral reflection (PHASR) scanner to obtain the in vivo THz-TDS images. We used the energy to Shannon entropy ratio of the wavelet packet coefficients of the THz-TDS waveforms on day 0 to create supervised support vector machine (SVM) classification models. Histological assessments of the burn biopsies serve as the ground truth.
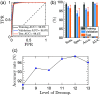
Results: We achieved an accuracy rate of 94.7% in predicting the wound healing outcome, as determined by histological measurement of the re-epithelialization rate on day 28 post-burn induction, using the THz-TDS measurements obtained on day 0. Furthermore, we report the accuracy rates of 89%, 87.1%, and 87.6% in automatic diagnosis of the superficial partial-thickness, deep partial-thickness, and full-thickness burns, respectively, using a multiclass SVM model.
Conclusions: The THz PHASR scanner promises a robust, high-speed, and accurate diagnostic modality to improve the clinical triage of burns and their management.
Keywords: Shannon entropy; burn assessment; machine learning; terahertz spectroscopic imaging; terahertz time-domain spectroscopy; wavelet packet transform.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Supervised machine learning for automatic classification of in vivo scald and contact burn injuries using the terahertz Portable Handheld Spectral Reflection (PHASR) Scanner.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 24;12(1):5096. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-08940-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35332207 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Assessment and Monitoring of Burn Wounds Using a Handheld Terahertz Hyperspectral Scanner.Adv Photonics Res. 2022 May;3(5):2100095. doi: 10.1002/adpr.202100095. Epub 2022 Jan 17. Adv Photonics Res. 2022. PMID: 36589697 Free PMC article.
-
Deep neural network classification of in vivo burn injuries with different etiologies using terahertz time-domain spectral imaging.Biomed Opt Express. 2022 Mar 3;13(4):1855-1868. doi: 10.1364/BOE.452257. eCollection 2022 Apr 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2022. PMID: 35519269 Free PMC article.
-
[Applications of terahertz spectroscopy in illicit drugs detection].Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi. 2013 Sep;33(9):2348-53. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi. 2013. PMID: 24369629 Review. Chinese.
-
Assessment of burn depth and burn wound healing potential.Burns. 2008 Sep;34(6):761-9. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2008.01.009. Epub 2008 Jun 3. Burns. 2008. PMID: 18511202 Review.
Cited by
-
Spatial attention-based residual network for human burn identification and classification.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 2;13(1):12516. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39618-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37532880 Free PMC article.
-
Triage of in vivo burn injuries and prediction of wound healing outcome using neural networks and modeling of the terahertz permittivity based on the double Debye dielectric parameters.Biomed Opt Express. 2023 Jan 30;14(2):918-931. doi: 10.1364/BOE.479567. eCollection 2023 Feb 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2023. PMID: 36874480 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo terahertz sensing of psoriasis and eczema patients.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 30;14(1):17546. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68106-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39079961 Free PMC article.
-
Terahertz polarimetric imaging of biological tissues: Monte Carlo modeling of signal contrast mechanisms due to Mie scattering.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 14:rs.3.rs-3745690. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3745690/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Biomed Opt Express. 2024 Mar 13;15(4):2328-2342. doi: 10.1364/BOE.515623. PMID: 38168438 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Terahertz Mie scattering in tissue: diffuse polarimetric imaging and Monte Carlo validation in highly attenuating media models.J Biomed Opt. 2025 Jun;30(6):066001. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.30.6.066001. Epub 2025 Jun 4. J Biomed Opt. 2025. PMID: 40474939 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization, “Burns,” 2018, https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/burns.

