MicroRNA Expression Profile Changes in the Leukocytes of Parkinson's Disease Patients
- PMID: 36348717
- PMCID: PMC9611861
- DOI: 10.32607/actanaturae.11729
MicroRNA Expression Profile Changes in the Leukocytes of Parkinson's Disease Patients
Abstract
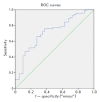
Parkinson's disease (PD) is one of the most common movement disorders. It is primarily diagnosed clinically. A correct diagnosis of PD in its early stages is important for the development of a pathogenic treatment, which necessitates a search for potential biomarkers of the disease. We evaluated the diagnostic value of several microRNAs and their relationship with the clinical characteristics of PD. The study included 70 PD patients and 40 healthy volunteers. We analyzed the expression of 15 microRNAs in blood leukocytes, which were selected based on literature data and modern concepts of molecular PD pathogenesis. All patients were evaluated using the Hoehn and Yahr scale, UPDRS, NMSQ, and PDQ-39. The data analysis revealed a statistically significant increase in the expression of miR-7-5p, miR-29c-3p, and miR-185-5p and a statistically significant decrease in the expression of miR-29a-3p and miR-30c-1-5p in leukocytes in PD. However, the altered microRNA profile was shown to have a moderate diagnostic value for PD diagnosis. MicroRNA expression changes were associated with the motor and non-motor phenotypic features of PD and administration of anti-Parkinson's drugs. Also, a relationship between some of the microRNAs studied and the duration and severity of PD was found, which may potentially be used to monitor disease progression.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; biomarkers; microRNA.
Copyright ® 2022 National Research University Higher School of Economics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aberrant expression of microRNA-132-3p and microRNA-146a-5p in Parkinson's disease patients.Open Life Sci. 2020 Sep 2;15(1):647-653. doi: 10.1515/biol-2020-0060. eCollection 2020. Open Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 33817253 Free PMC article.
-
Serum microRNA expression levels in Turkish patients with Parkinson's disease.Int J Neurosci. 2021 Dec;131(12):1181-1189. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2020.1784165. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Int J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 32546033
-
Differential expression and significance of miRNAs in plasma extracellular vesicles of patients with Parkinson's disease.Int J Neurosci. 2022 Jul;132(7):673-688. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2020.1835899. Epub 2020 Oct 26. Int J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 33045885
-
State of the Art of microRNAs Signatures as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets in Parkinson's and Alzheimer's Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 7;11(4):1113. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041113. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Evidence in Epigenomics and Proteomics Biomarkers for Early and Minimally Invasive Diagnosis of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Diseases.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(8):1273-1303. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666201223154009. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33357195 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Parkinson's disease patients combined with constipation tend to have higher serum expression of microRNA 29c, prominent neuropsychiatric disorders, possible RBD conversion, and a substandard quality of life.Neurol Sci. 2023 Sep;44(9):3141-3150. doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-06793-x. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Neurol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37067722
References
-
- Rizzo G., Copetti M., Arcuti S., Martino D., Fontana A., Logroscino G.. Neurology. 2016;86(6):566–576. - PubMed
-
- Gerasimou G., Costa D.C., Papanastasiou E., Bostanjiopoulou S., Arnaoutoglou M., Moralidis E., Aggelopoulou T., Gotzamani-Psarrakou A., Ann. Nucl. Med. Japan. 2012;26(4):337–344. - PubMed
-
- Arena J.E., Stoessl A.J.. Parkinsonism and Related Disorders. 2016;22:S47–S51. - PubMed
-
- Lang A.E., Espay A.J.. Movement Disorders. 2018;33(5):660–677. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources