Streamlining referral decisions for childhood poisoning: a cross-sectional study from a tertiary children's hospital in Cape Town, South Africa
- PMID: 36348737
- PMCID: PMC9634013
- DOI: 10.1016/j.afjem.2022.10.008
Streamlining referral decisions for childhood poisoning: a cross-sectional study from a tertiary children's hospital in Cape Town, South Africa
Abstract
Introduction: The study objectives were to report on current paediatric poisoning figures from South Africa, and to better understand this patient population to contribute suggestions for streamlining local triage and referral criteria.
Methods: A retrospective review of children presenting to Red Cross War Memorial Children's Hospital (RCWMCH) with poisoning between January 2009 and December 2019 was performed. Data were extracted from the Poisons Information Centre's Clinical Poisonings Database.
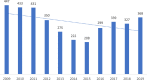
Results: There were 3699 incidents, involving 3662 patients; 3011 (81%) patients were under 5 years (median 29 months, IQR 19 to 49 months). There was a slight decline in numbers over the 11-year period.Most patients were referred (n = 2542, 69%), which included a greater proportion that were symptomatic (p < 0.001). There were 8 deaths (case fatality rate 0.2%).Medications were the most common single toxin group (n = 1270, 38%), followed by handyman and industrial (HI) products (n = 889, 27%), household products (n = 451, 14%), and pesticides (n = 445, 13%). There was a significant relationship between toxin type and referral patterns (p < 0.001) as well as clinical severity (p < 0.001): pesticides and HI products (paraffin, n = 486/568, 86%) had a greater proportion of referrals, and pesticides more moderate to fatal poisonings (n = 132/445, 30%), all due to cholinergic (organophosphates and carbamates) and formamidine pesticides.The medication subgroups anticonvulsants (n = 21/78, 27%), anti-infectives (n = 4/34, 12%), multi-vitamin/mineral (MVM) supplements (n = 17/84, 20%), neuropsychiatric medications (n = 50/350, 14%) and substances of abuse (n = 13/47, 28%) had larger proportions of moderate to severe poisonings (p < 0.001), as did the small group of biological toxins (n = 17/55, 31%; p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Certain medication, pesticide, and biological toxin subgroups, should be flagged for early referral. The goal is to improve patient outcomes as well as optimize the use of limited resources.
Keywords: Household product poisoning; Paraffin ingestion; Pediatric poisoning; Pesticide poisoning.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of African Federation for Emergency Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Global Burden of Disease (GBD) Compare, https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-compare/ [accessed June 2022].
-
- University of Cape Town, Faculty of Health Sciences, Department of Paediatrics, Poisons Information Centre Annual Reports, http://www.paediatrics.uct.ac.za/sites/default/files/image_tool/images/3... [accessed June 2022].
-
- World Bank Country and Lending Groups, https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-b... [accessed June 2022].
-
- Emergency Medicine Society of South Africa (ESSA). South African triage scale, https://emssa.org.za/special-interest-groups/the-south-african-triage-sc... [accessed June 2022].
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources