In situ Preparation of a Phospholipid Gel Co-Loaded with Methotrexate and Dexamethasone for Synergistic Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
- PMID: 36348765
- PMCID: PMC9637340
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S384772
In situ Preparation of a Phospholipid Gel Co-Loaded with Methotrexate and Dexamethasone for Synergistic Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by arthrocele, cartilage damage and disability. Although several anti-RA drugs have been developed for long-term treatment, they require frequent local injection and lead to multiple adverse effects such as osteoporosis and myelosuppression.
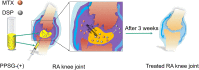
Purpose: Reducing the amount and frequency of anti-RA drugs methotrexate (MTX) and dexamethasone sodium phosphate (DSP) by local injection of phospholipid-based phase separation gel (PPSG) coloaded the two drugs, which presented PPSG-(+).
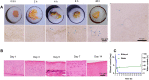
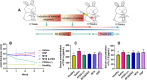
Methods: First, We characterized PPSG-(+). And we used UV spectrophotometry and high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to detect drug concentration, which can clarify the drug release in vitro and in vivo, respectively. We also injected PPSG-(+) into the joint cavity of healthy rabbits to prove the safety of PPSG-(+). Then, we injected PPSG-(+) into the joint cavity of RA modeled rabbits to demonstrate the effect in anti-RA of PPSG-(+) including the thickness of joints, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-1β detection, hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining and computed tomography (CT) of joints.
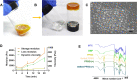
Results: Suspended particles show a tight and uniform arrangement in PPSG-(+). The gel underwent a phase transition at 20 min in vitro and 8 h in vivo, and vesicular structures reflecting its degradation and phase transition were observed in vivo. PPSG-(+) released both drugs in a sustained and fixed ratio for more than 14 days, while it proved to be safe for intra-articular injection and did not induce inflammation in a rabbit. Eventually, PPSG-(+) showed a good anti-RA effect and its potency can be maintained for 3 weeks.
Conclusion: PPSG-(+) is a drug delivery system offering good biocompatibility and sustained release of MTX and DSP, leading to long-lasting anti-RA effect.
Keywords: anti rheumatoid arthritis; drug delivery system; in situ gel; sustained release.
© 2022 Pu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A sustained-release phospholipid-based phase separation gel loaded with berberine for treating rheumatoid arthritis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jul 20;14:1210129. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1210129. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37547331 Free PMC article.
-
Injectable and biodegradable phospholipid-based phase separation gel for sustained delivery of insulin.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019 Apr 1;176:194-201. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.01.003. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019. PMID: 30616110
-
Thymopentin-loaded phospholipid-based phase separation gel with long-lasting immunomodulatory effects: in vitro and in vivo studies.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019 Apr;40(4):514-521. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0085-8. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019. PMID: 30002492 Free PMC article.
-
Improving dexamethasone drug loading and efficacy in treating rheumatoid arthritis via liposome: Focusing on inflammation and molecular mechanisms.Animal Model Exp Med. 2025 Jan;8(1):5-19. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12518. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Animal Model Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 39627850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural joint damage and hand bone loss in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Dan Med J. 2018 Mar;65(3):B5452. Dan Med J. 2018. PMID: 29510810 Review.
Cited by
-
The Advances in Phospholipids-Based Phase Separation Gels for the Sustained Release of Peptides, Proteins, and Chemotherapeutics.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jun 29;16(7):875. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070875. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39065572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology-empowered combination therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: principles, strategies, and challenges.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jul 22;22(1):431. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02670-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39034407 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lieben L. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:18002. - PubMed
-
- Sparks JA. Rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 2019;170(1):ITC1–ITC16. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2016;388(10055):2023–2038. - PubMed
-
- Burmester GR, Pope JE. Novel treatment strategies in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2017;389(10086):2338–2348. - PubMed
-
- Goksel Y, Zor K, Rindzevicius T, Thorhauge A-NBE, Schmiegelow K, Boisen A. Quantification of methotrexate in human serum using surface-enhanced raman scattering-toward therapeutic drug monitoring. ACS Sens. 2021;6(7):2664–2673. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

