Cynara cardunculus as a potential source of milk coagulating protease: Effects on physical properties of cow's milk
- PMID: 36348785
- PMCID: PMC9632194
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.2981
Cynara cardunculus as a potential source of milk coagulating protease: Effects on physical properties of cow's milk
Abstract
In the present research study, Cynara cardunculus (wild cardoon) flowers were blended and extracted using different types of buffers (phosphate buffer; citrate buffer and distilled water) for different maceration times. The most reliable, quick and efficient buffer was found to be phosphate (pH = 6.5) with a 6-h maceration time, which was used throughout this study. C. cardunculus extract (CE) was found to have high clotting and proteolytic activities. The extracted enzyme was found to be very stable against a wide range of pH values as well as of temperature. The formation of milk gels prepared in the presence of CE with different types of milk was evaluated using dynamic rheology and Turbiscan. The evolution of both elastic (G') and viscous (G″) moduli was monitored with time. The values of the whole milk enriched with milk powder gels were higher. Coagulum stability was evaluated using Turbiscan. The textural properties and the curd-firming rate of coagulum were also determined. In conclusion, the prepared CE could be an efficient milk-clotting agent in the production of dairy products.
Keywords: Cynara extract; coagulation; milk; rheology; stability; texture; wild cardoon.
© 2022 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

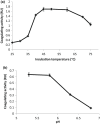
 ); pH = 6.5 (
); pH = 6.5 ( ) and pH = 5.9 (
) and pH = 5.9 ( )
)


Similar articles
-
Effect of extraction pH on techno-functional properties of crude extracts from wild cardoon (Cynara cardunculus L.) flowers.Food Chem. 2017 Jun 15;225:258-266. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.01.040. Epub 2017 Jan 10. Food Chem. 2017. PMID: 28193423
-
Technological properties of milk gels produced by chymosin and wild cardoon rennet optimized by response surface methodology.Food Chem. 2017 Dec 15;237:150-158. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.05.105. Epub 2017 May 19. Food Chem. 2017. PMID: 28763981
-
Toward alternative sources of milk coagulants for cheese manufacturing: establishment of hairy roots culture and protease characterization from Cynara cardunculus L.Plant Cell Rep. 2020 Jan;39(1):89-100. doi: 10.1007/s00299-019-02475-1. Epub 2019 Oct 3. Plant Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 31583429
-
Cardoon-based rennets for cheese production.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Jun;102(11):4675-4686. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9032-3. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29696340 Review.
-
Future Perspective and Technological Innovation in Cheese Making Using Artichoke (Cynara scolymus) as Vegetable Rennet: A Review.Foods. 2023 Aug 12;12(16):3032. doi: 10.3390/foods12163032. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37628031 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adetunji, V. O. , & Salawu, O. T. (2008). West African soft cheese ‘wara’ processed with Calotropis procera and Carica papaya: A comparative assessment of nutritional values. African Journal of Biotechnology, 7, 3360–3362.
-
- Agboola, S. O. , Chan, H. H. , Zhao, J. , & Rehman, A. (2009). Can the use of Australian cardoon (Cynara cardunculus L.) coagulant overcome the quality problems associated with cheese made from ultrafiltered milk? LWT–Food Science and Technology, 42, 1352–1359.
-
- Barros, R. , Ferreira, C. A. , Silva, S. V. , & Malcata, F. (2001). Quantitative studies on the enzymatic hydrolysis of milk protein brought about cardosins precipitated by ammonium sulfate. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 29, 541–574.
-
- Ben Amira, A. , Blecker, C. , Richel, A. , Fickers, P. , Francise, F. , Besbes, S. , & Attia, H. (2018). Influence of the ripening stage and the lyophilization of wild cardoon flowers on their chemical composition, enzymatic activities of extracts and technological properties of cheese curds. Food Chemistry, 245, 919–925. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

