The Impact of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-2 (ACE-2) on Bone Remodeling Marker Osteoprotegerin (OPG) in Post-COVID-19 Iraqi Patients
- PMID: 36348825
- PMCID: PMC9633432
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.29926
The Impact of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-2 (ACE-2) on Bone Remodeling Marker Osteoprotegerin (OPG) in Post-COVID-19 Iraqi Patients
Abstract
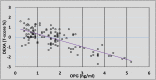
Introduction As COVID-19 affects human genes in several types of peripheral tissue, numerous disorders occur after recovery. The virus enters host cells via angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2) receptors that affect bone remodeling, leading to osteopenia or osteoporosis, which is characterized by low bone mineral density (BMD). The adult skeleton undergoes about 10% remodeling annually, which is crucial for preventing fatigue damage and preserving calcium homeostasis. An imbalance in the rates of bone production and resorption causes bone loss. Osteoprotegerin (OPG) is one of the regulators involved in the bone remodeling mechanism, it decreases the activity of NF-B receptors that activates the receptor activators of NF-B ligand (RANKL) pathway, which maintains the bone homeostasis balance. This study aims to find out the disruption of bone homeostasis balance in Iraqi post-COVID-19 patients. Materials and methods It is a case-control study that includes 130 Iraqi subjects enrolled. They were divided into two groups - the first group consisted of 80 post-COVID-19 infection patients, while the second group consisted of 50 who were not infected with COVID-19. Also, the levels of ACE-2 and OPG were measured in the serum by the ELISA technique. The BMD was measured by the DEXA scan technique. Results This study found that there is an effect of coronavirus infection on the bone strength measured by the Mean of the OPG level, which was found to be highly significant in the serum of post-COVID-19 patients when compared with non-COVID-19 subjects (P-value = 0.001), but the Mean of ACE-2 level was statistically non-significant between the two groups (P-value = 0.13). Also, the BMD of post-COVID-19 patients that was measured by DEXA scan had a statistically highly significant T-score% between the two groups. Conclusion The current study found that there was an effect of COVID-19 on the bone remodeling mechanism, which may be causing osteopenia or osteoporosis for Iraqi subjects enrolled in the current study. Also, analyzing the OPG level in the serum could be helpful in predicting low BMD.
Keywords: ace-2; covid-19; dexa scan; opg; osteoporosis.
Copyright © 2022, AL-Azzawi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changes in the RANK ligand/osteoprotegerin system are correlated to changes in bone mineral density in bisphosphonate-treated osteoporotic patients.Osteoporos Int. 2006;17(5):693-703. doi: 10.1007/s00198-005-0035-4. Epub 2006 Jan 25. Osteoporos Int. 2006. PMID: 16435076 Clinical Trial.
-
Circulating osteoprotegerin and leptin levels in postmenopausal women with and without osteoporosis.Rom J Intern Med. 2003;41(4):409-15. Rom J Intern Med. 2003. PMID: 15526523
-
Association between low bone mass and the serum RANKL and OPG in patients with nephrolithiasis.BMC Nephrol. 2018 Jul 11;19(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12882-018-0960-z. BMC Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29996796 Free PMC article.
-
[Bone remodeling and mineral homeostasis].Clin Calcium. 2006 Jan;16(1):46-53. Clin Calcium. 2006. PMID: 16397350 Review. Japanese.
-
Role of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand and osteoprotegerin in bone cell biology.J Mol Med (Berl). 2001 Jun;79(5-6):243-53. doi: 10.1007/s001090100226. J Mol Med (Berl). 2001. PMID: 11485016 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of hormones in bone remodeling in the craniofacial complex: A review.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2023 Mar-Apr;13(2):210-217. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2023.01.009. Epub 2023 Jan 21. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2023. PMID: 36718389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Relationship between Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS) Activity, Osteoporosis and Estrogen Deficiency in Type 2 Diabetes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 26;24(15):11963. doi: 10.3390/ijms241511963. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 and Bone Loss: A Review of Risk Factors, Mechanisms, and Future Directions.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2024 Feb;22(1):122-134. doi: 10.1007/s11914-023-00842-2. Epub 2024 Jan 15. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2024. PMID: 38221578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in research on osteoporosis secondary to SARS-CoV-2 infection.Animal Model Exp Med. 2025 May;8(5):829-841. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12573. Epub 2025 Mar 3. Animal Model Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 40029778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
OPG and BAFF as predictive biomarkers of the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Feb;29(3):e70189. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70189. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39888266 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mechanisms of COVID-19 entry into the cell: potential therapeutic approaches based on virus entry inhibition in COVID-19 patients with underlying diseases. Musavi H, Abazari O, Safaee MS, et al. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021;20:11–23. - PubMed
-
- How the coronavirus infects cells - and why Delta is so dangerous. Scudellari M. Nature. 2021;595:640–644. - PubMed
-
- Serum osteocalcin and serum osteopontin levels in osteoporotic postmenopausal women with and without vertebral fractures. Mohammed N, Turki K, Munshed M. J Fac Med. 2015;57:257–262.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous