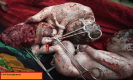
Lethal Cord Entanglement
- PMID: 36349075
- PMCID: PMC9631348
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.31047
Lethal Cord Entanglement
Abstract
Cord entanglement and conjoined twins are unique complications of monoamniotic monochorionic pregnancy. This case report describes a case of monoamniotic twins' intrauterine demise due to lethal cord entanglement. A 26-year-old unbooked primigravida was reported in the emergency labor room at 32 weeks with the complaint of loss of fetal movements since the previous day. On obstetric examination, the uterus appeared enlarged and discordant with the gestational age, multiple fetal parts were felt on palpation, and the pelvic grip was empty. Doppler could not detect any fetal heartbeat. The emergency obstetric sonography scan showed twins, the first in breech and the second in vertex presentation. Fetal heart sound was not found for either of the twins. The patient was counseled, and the decision was taken to terminate the pregnancy by lower-segment cesarean section. During the cesarean to deliver the babies, monochorionic and monoamniotic pregnancy was confirmed.
Keywords: antenatal care; monoamniotic twins; monochorionic monoamniotic twins; twin pregnancy; umbilical cord entanglement.
Copyright © 2022, Hans et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Zygotic-splitting rates after single-embryo transfers in in vitro fertilization. Blickstein I, Jones C, Keith LG. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2366–2367. - PubMed
-
- What makes them split? Identifying risk factors that lead to monozygotic twins after in vitro fertilization. Knopman JM, Krey LC, Oh C, Lee J, McCaffrey C, Noyes N. Fertil Steril. 2014;102:82–89. - PubMed
-
- Assisted reproductive technologies and monozygous twins: implications for future study and clinical practice. Sills ES, Tucker MJ, Palermo GD. Twin Res. 2000;3:217. - PubMed
-
- Monoamniotic twinning and zona manipulation: a survey of U.S. IVF centers correlating zona manipulation procedures and high-risk twinning frequency. Slotnick RN, Ortega JE. J Assist Reprod Genet. 1996;13:381–385. - PubMed
-
- Monoamniotic and pseudomonoamniotic twins: sonographic diagnosis, detection of cord entanglement, and obstetric management. Aisenbrey GA, Catanzarite VA, Hurley TJ, et al. Obstet Gynecol. 1995;86:218. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources