Determination of binding affinity of tunicamycin with SARS-CoV-2 proteins: Proteinase, protease, nsp2, nsp9, ORF3a, ORF7a, ORF8, ORF9b, envelope and RBD of spike glycoprotein
- PMID: 36349218
- PMCID: PMC9633632
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vacun.2022.10.006
Determination of binding affinity of tunicamycin with SARS-CoV-2 proteins: Proteinase, protease, nsp2, nsp9, ORF3a, ORF7a, ORF8, ORF9b, envelope and RBD of spike glycoprotein
Abstract
Introduction: Despite the availability of several COVID-19 vaccines, the incidence of infections remains a serious issue. Tunicamycin (TM), an antibiotic, inhibited tumor growth, reduced coronavirus envelope glycoprotein subunit 2 synthesis, and decreased N-linked glycosylation of coronavirus glycoproteins.
Objectives: Our study aimed to determine how tunicamycin interacts with certain coronavirus proteins (proteinase, protease, nsp9, ORF7a, ORF3a, ORF9b, ORF8, envelope protein, nsp2, and RBD of spike glycoprotein). Methods: Several types of chemo and bioinformatics tools were used to achieve the aim of the study. As a result, virion's effectiveness may be impaired.
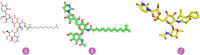
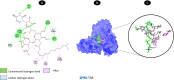
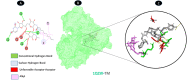
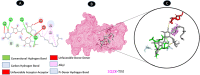
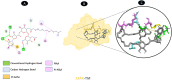
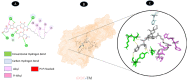
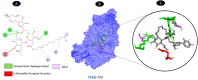
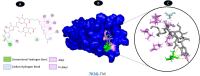
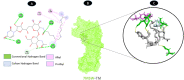
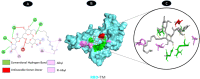
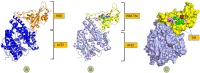
Results: TM can bind to viral proteins with various degrees of affinity. The proteinase had the highest binding affinity with TM. Proteins (ORF9b, ORF8, nsp9, and RBD) were affected by unfavorable donor or acceptor bonds that impact the degree of docking. ORF7a had the weakest affinities.
Conclusions: This antibiotic is likely to effect on SARS-CoV-2 in clinical studies.
Introducción: A pesar de la disponibilidad de varias vacunas contra la COVID-19, la incidencia de infecciones sigue siendo un problema grave. La tunicamicina (TM), un antibiótico, inhibió el crecimiento tumoral, redujo la síntesis de la subunidad 2 de la glicoproteína de la envoltura del coronavirus y disminuyó la glicosilación ligada a N de las glicoproteínas del coronavirus.
Objetivos: Nuestro estudio tuvo como objetivo determinar cómo interactúa la tunicamicina con ciertas proteínas del coronavirus (proteinasa, proteasa, nsp9, ORF7a, ORF3a, ORF9b, ORF8, proteína de la envoltura, nsp2 y RBD de glicoproteína de punta).
Métodos: Se utilizaron varios tipos de herramientas de quimioterapia y bioinformática para lograr el objetivo del estudio. Como resultado, la eficacia del virión puede verse afectada.
Resultados: La TM puede unirse a proteínas virales con diversos grados de afinidad. La proteinasa tenía la mayor afinidad de unión con TM. Las proteínas (ORF9b, ORF8, nsp9 y RBD) se vieron afectadas por enlaces donantes o aceptores desfavorables que afectan el grado de acoplamiento. ORF7a tenía las afinidades más débiles.
Conclusiones: Es probable que este antibiótico tenga efecto sobre el SARS-CoV-2 en estudios clínicos.
Keywords: COVID-19; Docking; Envelope; Spike; Tunicamycin.
© 2022 Elsevier España, S.L.U. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Woo P.C., Lau S.K., Laml C.S. Discovery of seven novel mammalian and avian coronaviruses in deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of alphacoronavirus and Betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of gammacoronavirus and deltacoronavirus. J Virol. 2012;86(7):3995–4008. doi: 10.1128/jvi.06540-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants. 2021. https://www.who.int/en/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants/ Accessed 10 February 2022.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
