STATISTICAL INFERENCE IN QUANTILE REGRESSION FOR ZERO-INFLATED OUTCOMES
- PMID: 36349247
- PMCID: PMC9640181
- DOI: 10.5705/ss.202020.0368
STATISTICAL INFERENCE IN QUANTILE REGRESSION FOR ZERO-INFLATED OUTCOMES
Abstract
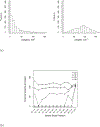
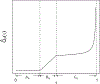
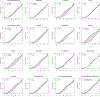
An extension of quantile regression is proposed to model zero-inflated outcomes, which have become increasingly common in biomedical studies. The method is flexible enough to depict complex and nonlinear associations between the covariates and the quantiles of the outcome. We establish the theoretical properties of the estimated quantiles, and develop inference tools to assess the quantile effects. Extensive simulation studies indicate that the novel method generally outperforms existing zero-inflated approaches and the direct quantile regression in terms of the estimation and inference of the heterogeneous effect of the covariates. The approach is applied to data from the Northern Manhattan Study to identify risk factors for carotid atherosclerosis, measured by the ultrasound carotid plaque burden.
Keywords: Constrained post-estimation smoothing; Nonnormal asymptotic distribution; Quantile regression; Zero-inflated outcomes.
Figures
References
-
- Chernozhukov V, Fernández-Val I, and Galichon A (2010). Quantile and probability curves without crossing. Econometrica 78(3), 1093–1125.
-
- Duan N, Manning WG, Morris CN, and Newhouse JP (1983). A comparison of alternative models for the demand for medical care. Journal of Business & Economic Statistics 1, 115–126.
-
- He X and Ng P (1999). Cobs: Qualitatively constrained smoothing via linear programming. Computational Statistics 14, 315–338.
-
- Heras A, Moreno I, and Vilar-Zanón JL (2018). An application of two-stage quantile regression to insurance ratemaking. Scandinavian Actuarial Journal 2018(9), 753–769.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
