Consensus guidelines for sarcopenia prevention, diagnosis and management in Australia and New Zealand
- PMID: 36349684
- PMCID: PMC9891980
- DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.13115
Consensus guidelines for sarcopenia prevention, diagnosis and management in Australia and New Zealand
Abstract
Background: Sarcopenia is an age-associated skeletal muscle condition characterized by low muscle mass, strength, and physical performance. There is no international consensus on a sarcopenia definition and no contemporaneous clinical and research guidelines specific to Australia and New Zealand. The Australian and New Zealand Society for Sarcopenia and Frailty Research (ANZSSFR) Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Management Task Force aimed to develop consensus guidelines for sarcopenia prevention, assessment, management and research, informed by evidence, consumer opinion, and expert consensus, for use by health professionals and researchers in Australia and New Zealand.
Methods: A four-phase modified Delphi process involving topic experts and informed by consumers, was undertaken between July 2020 and August 2021. Phase 1 involved a structured meeting of 29 Task Force members and a systematic literature search from which the Phase 2 online survey was developed (Qualtrics). Topic experts responded to 18 statements, using 11-point Likert scales with agreement threshold set a priori at >80%, and five multiple-choice questions. Statements with moderate agreement (70%-80%) were revised and re-introduced in Phase 3, and statements with low agreement (<70%) were rejected. In Phase 3, topic experts responded to six revised statements and three additional questions, incorporating results from a parallel Consumer Expert Delphi study. Phase 4 involved finalization of consensus statements.
Results: Topic experts from Australia (n = 62, 92.5%) and New Zealand (n = 5, 7.5%) with a mean ± SD age of 45.7 ± 11.8 years participated in Phase 2; 38 (56.7%) were women, 38 (56.7%) were health professionals and 27 (40.3%) were researchers/academics. In Phase 2, 15 of 18 (83.3%) statements on sarcopenia prevention, screening, assessment, management and future research were accepted with strong agreement. The strongest agreement related to encouraging a healthy lifestyle (100%) and offering tailored resistance training to people with sarcopenia (92.5%). Forty-seven experts participated in Phase 3; 5/6 (83.3%) revised statements on prevention, assessment and management were accepted with strong agreement. A majority of experts (87.9%) preferred the revised European Working Group for Sarcopenia in Older Persons (EWGSOP2) definition. Seventeen statements with strong agreement (>80%) were confirmed by the Task Force in Phase 4.
Conclusions: The ANZSSFR Task Force present 17 sarcopenia management and research recommendations for use by health professionals and researchers which includes the recommendation to adopt the EWGSOP2 sarcopenia definition in Australia and New Zealand. This rigorous Delphi process that combined evidence, consumer expert opinion and topic expert consensus can inform similar initiatives in countries/regions lacking consensus on sarcopenia.
Keywords: Aged; Geriatric assessment; Mass screening; Sarcopenia.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society on Sarcopenia, Cachexia and Wasting Disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
ABM has received speaker and consulting fees from Abbott, Nutricia, AstraZeneca, Novartis. GD is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of TSI, Abbott and Amgen and has received speaker/consulting fees from Amgen, Abbott and TSI. MG has received research funding from Bayer Pharma, Novartis, Weight Watchers, Lilly, Otsuka and speaker's honoraria from Bayer Pharma, Besins Healthcare, and Amgen. RMD reports a grant form Fonterra Co‐operative Group Ltd, honoraria for presentations from Abbott Australia and Nutricia Research and to serve as a member of an expert advisory committee. RV has previously received education and honorarium from the following Abbott, Nestle and Nutricia. SI has received speaker/consulting fees from Abbott, UK Dairy Council, European Milk Forum, Nestle Health Science and the Israel Milk Board.
Figures




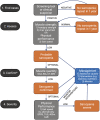
References
-
- Cruz‐Jentoft AJ, Sayer AA. Sarcopenia. Lancet 2019;393:2636–2646. - PubMed
-
- Pacifico J, Geerlings MAJ, Reijnierse EM, Phassouliotis C, Lim WK, Maier AB. Prevalence of sarcopenia as a comorbid disease: A systematic review and meta‐analysis. Exp Gerontol 2019;131:110801. - PubMed
-
- Papadopoulou SK, Tsintavis P, Potsaki G, Papandreou D. Differences in the Prevalence of Sarcopenia in Community‐Dwelling, Nursing Home and Hospitalized Individuals. A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis. J Nutr Health Aging 2020;24:83–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- GNT1174886/Australian National Health and Medical Research Council Investigator
- APP2005987/Australian Medical Research Future Fund
- CRE 1102208/NHMRC
- 2003179/NHMRC
- APP1099173/NHMRC
- APP1162867/NHMRC
- APP1199726/MRFF
- Deakin University
- Amgen
- Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS)
- Norman Beischer Foundation
- 102817/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- Australian Government Research Training Program
- CAF 130/2020/Royal Perth Hospital Career Advancement Fellowship
- Western Australian Future Health and Innovation Fund
- Dairy Australia
- California Dairy Research Foundation
- National Dairy Council
- Aarhus University Hospital
- Danish Dairy Research Foundation
- onterra Co-operative Group Ltd
- Dutch Dairy Association
- Dairy Council of California
- Dairy Farmers of Canada
- Centre national interprofessionnel de l'economie laitiere
- University of Melbourne
- Austin Hospital Medical Research Foundation
- Sir Edward Dunlop Medical Research Foundation
- Hospital Research Foundation
- 102817/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

