In Utero Enzyme-Replacement Therapy for Infantile-Onset Pompe's Disease
- PMID: 36351280
- PMCID: PMC10794051
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2200587
In Utero Enzyme-Replacement Therapy for Infantile-Onset Pompe's Disease
Abstract
Patients with early-onset lysosomal storage diseases are ideal candidates for prenatal therapy because organ damage starts in utero. We report the safety and efficacy results of in utero enzyme-replacement therapy (ERT) in a fetus with CRIM (cross-reactive immunologic material)-negative infantile-onset Pompe's disease. The family history was positive for infantile-onset Pompe's disease with cardiomyopathy in two previously affected deceased siblings. After receiving in utero ERT and standard postnatal therapy, the current patient had normal cardiac and age-appropriate motor function postnatally, was meeting developmental milestones, had normal biomarker levels, and was feeding and growing well at 13 months of age.
Copyright © 2022 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures
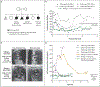
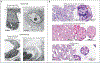

Comment in
-
Prenatal Enzyme-Replacement Therapy.N Engl J Med. 2022 Dec 8;387(23):2189-2193. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2211515. Epub 2022 Nov 9. N Engl J Med. 2022. PMID: 36351269 No abstract available.
References
-
- Platt FM. Emptying the stores: lysosomal diseases and therapeutic strategies. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2018; 17: 133–50. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen Q-H, Witt RG, Wang B, et al. Tolerance induction and microglial engraftment after fetal therapy without conditioning in mice with mucopolysaccharidosis type VII. Sci Transl Med 2020; 12(532): eaay8980. - PubMed
-
- Hamdan MA, El-Zoabi BA, Begam MA, Mirghani HM, Almalik MH. Antenatal diagnosis of Pompe disease by fetal echocardiography: impact on outcome after early initiation of enzyme replacement therapy. J Inherit Metab Dis 2010; 33: Suppl 3: S333–S339. - PubMed
-
- Ausems MG, Verbiest J, Hermans MP, et al. Frequency of glycogen storage disease type II in the Netherlands: implications for diagnosis and genetic counselling. Eur J Hum Genet 1999; 7: 713–6. - PubMed
