Curative islet and hematopoietic cell transplantation in diabetic mice without toxic bone marrow conditioning
- PMID: 36351397
- PMCID: PMC9922474
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111615
Curative islet and hematopoietic cell transplantation in diabetic mice without toxic bone marrow conditioning
Abstract
Mixed hematopoietic chimerism can promote immune tolerance of donor-matched transplanted tissues, like pancreatic islets. However, adoption of this strategy is limited by the toxicity of standard treatments that enable donor hematopoietic cell engraftment. Here, we address these concerns with a non-myeloablative conditioning regimen that enables hematopoietic chimerism and allograft tolerance across fully mismatched major histocompatibility complex (MHC) barriers. Treatment with an αCD117 antibody, targeting c-Kit, administered with T cell-depleting antibodies and low-dose radiation permits durable multi-lineage chimerism in immunocompetent mice following hematopoietic cell transplant. In diabetic mice, co-transplantation of donor-matched islets and hematopoietic cells durably corrects diabetes without chronic immunosuppression and no appreciable evidence of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Donor-derived thymic antigen-presenting cells and host-derived peripheral regulatory T cells are likely mediators of allotolerance. These findings provide the foundation for safer bone marrow conditioning and cell transplantation regimens to establish hematopoietic chimerism and islet allograft tolerance.
Keywords: CP: Cell biology; CP: Immunology; allogeneic transplantation; bone marrow; diabetes mellitus; hematopoietic cell transplantation; immunologic tolerance; islet transplantation; mixed chimerism.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.A.S. is a co-founder, stockholder, and board member and C.A.C. and H.-S.K. are employees and stockholders of Jasper Therapeutics, Inc.
Figures
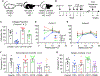
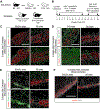
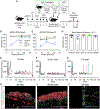
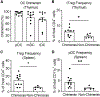
Comment in
-
Bone marrow chimerism breaks the barrier to pancreatic islet transplantation.Cell Rep. 2022 Nov 15;41(7):111692. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111692. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 36384104
References
-
- Agarwal R, Dvorak CC, Prockop S, Kwon H-S, Long-Boyle JR, Le A, Brown JW, Merkel E, Truong K, Velasco B, et al. (2021). JSP191 as a single-agent conditioning regimen results in successful engraftment, donor myeloid chimerism, and production of donor derived naïve lymphocytes in patients with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID). Blood 138, 554. 10.1182/blood-2021-153074. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

