Cardiac myosin-specific autoimmune T cells contribute to immune-checkpoint-inhibitor-associated myocarditis
- PMID: 36351411
- PMCID: PMC11108585
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111611
Cardiac myosin-specific autoimmune T cells contribute to immune-checkpoint-inhibitor-associated myocarditis
Abstract
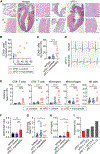
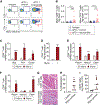
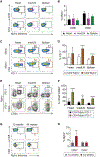
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are an effective therapy for various cancers; however, they can induce immune-related adverse events (irAEs) as a side effect. Myocarditis is an uncommon, but fatal, irAE caused after ICI treatments. Currently, the mechanism of ICI-associated myocarditis is unclear. Here, we show the development of myocarditis in A/J mice induced by anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) administration alone without tumor cell inoculation, immunization, or viral infection. Mice with myocarditis have increased cardiac infiltration, elevated cardiac troponin levels, and arrhythmia. Anti-PD-1 mAb treatment also causes irAEs in other organs. Autoimmune T cells recognizing cardiac myosin are activated and increased in mice with myocarditis. Notably, cardiac myosin-specific T cells are present in naive mice, showing a phenotype of antigen-experienced T cells. Collectively, we establish a clinically relevant mouse model for ICI-associated myocarditis and find a contribution of cardiac myosin-specific T cells to ICI-associated myocarditis development and pathogenesis.
Keywords: CP: Immunology; ICI; ICI-associated myocarditis; PD-1; autoimmune T cells; cardiac myosin; immune checkpoint inhibitor.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

