Comparison of short interval and low dose (SILD) with high dose of cyclophosphamide in the susceptibility to infection in SLE: a multicentrereal-world study
- PMID: 36351697
- PMCID: PMC9644361
- DOI: 10.1136/lupus-2022-000779
Comparison of short interval and low dose (SILD) with high dose of cyclophosphamide in the susceptibility to infection in SLE: a multicentrereal-world study
Abstract
Objective: Infection is a major cause of death in patients with SLE. This study aimed to explore the infection rate in patients with SLE receiving a low dose of intravenous cyclophosphamide (IV-CYC).
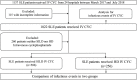
Methods: Clinical parameters of 1022 patients with SLE from 24 hospitals in China were collected. Patients were divided into the short-interval and lower-dose (SILD, 400 mg every 2 weeks) IV-CYC group and the high-dose (HD, 500 mg/m2 of body surface area every month) IV-CYC group. The clinical data and infection rate between the two groups were compared.
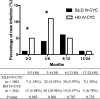
Results: Compared with HD IV-CYC, the infection rate of the SILD IV-CYC group was significantly lower (13.04% vs 22.27%, p=0.001). Respiratory tract infection (10.28% vs 15.23%, p=0.046) and skin/soft tissue infection (1.78% vs 4.3%, p=0.040) were significantly decreased in the SILD IV-CYC group. Moreover, infections occurred most likely in patients with SLE with leucopenia (OR 2.266, 95% CI 1.322 to 3.887, p=0.003), pulmonary arterial hypertension (OR 2.756, 95% CI 1.249 to 6.080, p=0.012) and >15 mg/day of glucocorticoid (OR 2.220, 95% CI 1.097 to 4.489, p=0.027).
Conclusions: SILD IV-CYC showed a lower frequency of infection events than high-dose IV-CYC in patients with SLE.
Keywords: SLE; cyclophosphamide; therapeutics.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
