Tetrahydroquinolinone derivatives exert antiproliferative effect on lung cancer cells through apoptosis induction
- PMID: 36352170
- PMCID: PMC9646836
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-23640-9
Tetrahydroquinolinone derivatives exert antiproliferative effect on lung cancer cells through apoptosis induction
Abstract
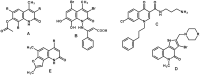
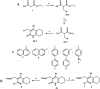
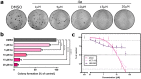
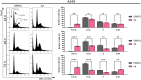
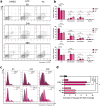
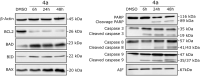
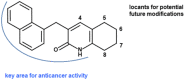
The anticancer properties of quinolones is a topic of interest among researchers in the scientific world. Because these compounds do not cause side effects, unlike the commonly used cytostatics, they are considered a promising source of new anticancer drugs. In this work, we designed a brief synthetic pathway and obtained a series of novel 8-phenyltetrahydroquinolinone derivatives functionalized with benzyl-type moieties at position 3. The compounds were synthesized via classical reactions such as nucleophilic substitution, solvent lysis, and condensation. Biological evaluation revealed that 3-(1-naphthylmethyl)-4-phenyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1H-quinolin-2-one (4a) exhibited potent cytotoxicity toward colon (HTC-116) and lung (A549) cancer cell lines. Analysis of the mechanism of action of compounds showed that compound 4a induced cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase, leading to apoptotic cell death via intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. Taken together, the findings of the study suggest that tetrahydroquinolinone derivatives bearing a carbonyl group at position 2 could be potential lead compounds to develop anticancer agents for the treatment of lung cancers.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Beberok A, et al. Ciprofloxacin triggers the apoptosis of human triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells via the p53/Bax/BCL-2 signaling pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2018;52:1727–1737. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

