Five waves of COVID-19 pandemic in Italy: results of a national survey evaluating the impact on activities related to arrhythmias, pacing, and electrophysiology promoted by AIAC (Italian Association of Arrhythmology and Cardiac Pacing)
- PMID: 36352300
- PMCID: PMC9646282
- DOI: 10.1007/s11739-022-03140-4
Five waves of COVID-19 pandemic in Italy: results of a national survey evaluating the impact on activities related to arrhythmias, pacing, and electrophysiology promoted by AIAC (Italian Association of Arrhythmology and Cardiac Pacing)
Abstract
Background: The subsequent waves of the COVID-19 pandemic in Italy had a major impact on cardiac care.
Methods: A survey to evaluate the dynamic changes in arrhythmia care during the first five waves of COVID-19 in Italy (first: March-May 2020; second: October 2020-January 2021; third: February-May 2021; fourth: June-October 2021; fifth: November 2021-February 2022) was launched.
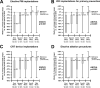
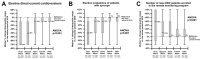
Results: A total of 127 physicians from arrhythmia centers (34% of Italian centers) took part in the survey. As compared to 2019, a reduction in 40% of elective pacemaker (PM), defibrillators (ICD), and cardiac resynchronization devices (CRT) implantations, with a 70% reduction for ablations, was reported during the first wave, with a progressive and gradual return to pre-pandemic volumes, generally during the third-fourth waves, slower for ablations. For emergency procedures (PM, ICD, CRT, and ablations), recovery from the initial 10% decline occurred in most cases during the second wave, with some variability. However, acute care for atrial fibrillation, electrical cardioversions, and evaluations for syncope showed a prolonged reduction of activity. The number of patients with devices which started remote monitoring increased by 40% during the first wave, but then the adoption of remote monitoring declined.
Conclusions: The dramatic and profound derangement in arrhythmia management that characterized the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic was followed by a progressive return to the volume of activities of the pre-pandemic periods, even if with different temporal dynamics and some heterogeneity. Remote monitoring was largely implemented during the first wave, but full implementation is needed.
Keywords: Ablation; Arrhythmia; Atrial fibrillation; COVID-19; Cardiac resynchronization therapy; Implantable cardioverter defibrillators; Pacemakers; Remote monitoring.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Medicina Interna (SIMI).
Conflict of interest statement
G Boriani: small speaker fees from Bayer, Boston, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Daiichi-Sankyo. F Guerra: small speaker fees from Bayer, Bristol-Meyers-Squibb, Boston, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Daiichi-Sankyo, and Zoll. M Bertini: small speaker fees from Boston Scientific, Abbott, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Bayer. M Landolina: modest speaker fees from Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Boston Scientific, LivaNova, Medtronic, and Pfizer. RP Ricci: small speaker fees by Boston e Biotronik; advisory board modest fees by Dompé. R De Ponti: lecture fees from Biosense Webster and Biotronik. P Palmisano: small speaker fees from Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Medtronic. Novartis and personal fees from Proctorship agreement with Abbott, Medtronic, Biotronik, and Boston Scientific. No conflicts of interest were reported by the other authors.
Figures



References
-
- Di Liberto IA, Pilato G, Geraci S, Milazzo D, Vaccaro G, Buccheri S, Caramanno G. Impact on hospital admission of ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients during coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic in an Italian Hospital. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown) 2020;21:722–724. doi: 10.2459/JCM.0000000000001053. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Task Force for the management of COVID-19 of the European Society of Cardiology (2022) European Society of Cardiology guidance for the diagnosis and management of cardiovascular disease during the COVID-19 pandemic: part 1-epidemiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis. Eur Heart J 43:1033–1058 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

