Temporal disambiguation of relative temporal expressions in clinical texts
- PMID: 36352893
- PMCID: PMC9638055
- DOI: 10.3389/frma.2022.1001266
Temporal disambiguation of relative temporal expressions in clinical texts
Abstract
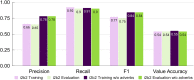
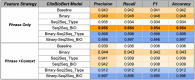
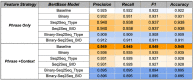
Temporal expression recognition and normalization (TERN) is the foundation for all higher-level temporal reasoning tasks in natural language processing, such as timeline extraction, so it must be performed well to limit error propagation. Achieving new heights in state-of-the-art performance for TERN in clinical texts requires knowledge of where current systems struggle. In this work, we summarize the results of a detailed error analysis for three top performing state-of-the-art TERN systems that participated in the 2012 i2b2 Clinical Temporal Relation Challenge, and compare our own home-grown system Chrono to identify specific areas in need of improvement. Performance metrics and an error analysis reveal that all systems have reduced performance in normalization of relative temporal expressions, specifically in disambiguating temporal types and in the identification of the correct anchor time. To address the issue of temporal disambiguation we developed and integrated a module into Chrono that utilizes temporally fine-tuned contextual word embeddings to disambiguate relative temporal expressions. Chrono now achieves state-of-the-art performance for temporal disambiguation of relative temporal expressions in clinical text, and is the only TERN system to output dual annotations into both TimeML and SCATE schemes.
Keywords: BERT; clinical text; contextual word embeddings; error analysis; natural language processing; relative temporal expression; temporal expression recognition and normalization; temporal reasoning.
Copyright © 2022 Olex and McInnes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Leveraging Temporal Trends for Training Contextual Word Embeddings to Address Bias in Biomedical Applications: Development Study.JMIR AI. 2024 Oct 2;3:e49546. doi: 10.2196/49546. JMIR AI. 2024. PMID: 39357045 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating machine learning with linguistic features: A universal method for extraction and normalization of temporal expressions in Chinese texts.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2023 May;233:107474. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2023.107474. Epub 2023 Mar 11. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2023. PMID: 36931017
-
Review of Temporal Reasoning in the Clinical Domain for Timeline Extraction: Where we are and where we need to be.J Biomed Inform. 2021 Jun;118:103784. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2021.103784. Epub 2021 Apr 14. J Biomed Inform. 2021. PMID: 33862232 Review.
-
Disambiguating Clinical Abbreviations Using a One-Fits-All Classifier Based on Deep Learning Techniques.Methods Inf Med. 2022 Jun;61(S 01):e28-e34. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1742388. Epub 2022 Feb 1. Methods Inf Med. 2022. PMID: 35104909 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal reasoning with medical data--a review with emphasis on medical natural language processing.J Biomed Inform. 2007 Apr;40(2):183-202. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2006.12.009. Epub 2007 Jan 11. J Biomed Inform. 2007. PMID: 17317332 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Almasian S., Aumiller D., Gertz M. (2022). BERT got a date: introducing transformers to temporal tagging. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2109.14927. 10.48550/arXiv.2109.14927 - DOI
-
- Alsentzer E., Murphy J. R., Boag W., Weng W.-H., Jin D., Naumann T., et al. . (2019). Publicly available clinical BERT embeddings. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1904.03323. 10.18653/v1/W19-1909 - DOI
-
- Bethard S., Parker J. (2016). A semantically compositional annotation scheme for time normalization, in Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (Portorož: European Language Resources Association; ), 3779–3786. Available online at: https://aclanthology.org/L16-1599/
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

