Essential oils of Zingiber officinale: Chemical composition, in vivo alleviation effects on TPA induced ear swelling in mice and in vitro bioactivities
- PMID: 36352904
- PMCID: PMC9639606
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1043175
Essential oils of Zingiber officinale: Chemical composition, in vivo alleviation effects on TPA induced ear swelling in mice and in vitro bioactivities
Abstract
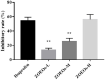
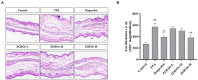
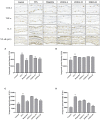
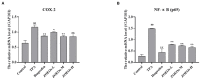
Zingiber officinale (ZO) is a traditional food condiment. The essential oils of Z. officinale (ZOEOs) are known to have multiple bioactivities. In this study, gas chromatography mass spectrometer (GC-MS) analytical method was used to identify active ingredient present in ZOEOs. A total of 41 compounds were identified in ZOEOs. Major components in ZOEOs were zingiberene (19.71%), (+)-β-cedrene (12.85%), farnesene (12.17%), α-curcumene (10.18%) and β-elemene (3.54%). Experimental results of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13 acetate (TPA) induced ear swelling validation mice model showed that ZOEOs treatment has better anti-inflammatory effect compared with ibuprofen (positive control) at high concentrations. Histological and immunohistochemical analysis showed that ZOEOs significantly decreased COX-2, IL-6 and NF-κB expression in a dose dependent manner. The mRNA levels of COX-2 and NF-κB were also down regulated by the application of ZOEOs. This indicated that ZOEOs exhibited positive effects in ear skin protection. Antibacterial experimental results showed that EOZOs had anti-bacterial effects on Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Staphylococcus aureus. DPPH radical scavenging, A549 cell line and LNCaP cell line inhibition results indicated that ZOEOs exhibited potential antioxidant and anti-tumor properties. The findings of these study provide scientific basis on therapeutic use of ZO in food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries.
Keywords: Zingiber officinale; anti-bacterial effects; anti-inflammation; anti-tumor property; antioxidation; edible spices; essential oil.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Zhang, Yu, Luo, Chen, Liu, Zhang, Zhang and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
Author SZ was employed by Shenzhen Precision Health Food Technology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Essential Oil of Zingiber cassumunar Roxb. and Zingiber officinale Rosc.: A Comparative Study on Chemical Constituents, Antibacterial Activity, Biofilm Formation, and Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing System.Chem Biodivers. 2023 Jun;20(6):e202201205. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202201205. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Chem Biodivers. 2023. PMID: 37202876
-
Chemical Profile, Antibacterial and Antioxidant Potential of Zingiber officinale Roscoe and Elettaria cardamomum (L.) Maton Essential Oils and Extracts.Plants (Basel). 2022 May 31;11(11):1487. doi: 10.3390/plants11111487. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35684260 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical composition, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of the essential oils from male and female specimens of Baccharis punctulata (Asteraceae).J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Apr 24;234:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.01.005. Epub 2019 Jan 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30660710
-
Essential Oils from Zingiber striolatum Diels Attenuate Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress through Regulation of MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Dec 19;10(12):2019. doi: 10.3390/antiox10122019. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943122 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative study on chemical compositions and biological activities of four essential oils: Cymbopogon citratus (DC.) Stapf, Cinnamomum cassia (L.) Presl, Salvia japonica Thunb. and Rosa rugosa Thunb.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Nov 15;280:114472. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114472. Epub 2021 Jul 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34332066
Cited by
-
Design and Evaluation of a Zingiber officinale-Kaolinite-Maltodextrin Delivery System: Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, and Cytotoxic Activity Assessment.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jun 6;17(6):751. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17060751. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40574063 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in plant essential oils and drug delivery systems for skincare.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 17;16:1578280. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1578280. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40313613 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee YS, Kang YJ, Ryu MJ. Antibacterial effect and deodorization effect of extracts from different parts of Z. officinale. Asian J Beauty Cosmetol. (2020) 18:521–31. 10.20402/ajbc.2020.0070 - DOI
-
- Crichton M, Marshall S, Marx W, Isenring E. Efficacy of ginger (Z. officinale) in ameliorating chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting and chemotherapy-related outcomes: a systematic literature review update and meta-analysis. J Acad Nutr Diet. (2018) 119:2055–68. 10.1016/j.jand.2019.06.009 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

