Tacrolimus Monotherapy is Safe in Immunologically Low-Risk Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Randomized-Controlled Pilot Study
- PMID: 36353052
- PMCID: PMC9637544
- DOI: 10.3389/ti.2022.10839
Tacrolimus Monotherapy is Safe in Immunologically Low-Risk Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Randomized-Controlled Pilot Study
Abstract
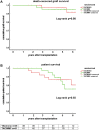
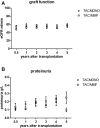
In this randomized-controlled pilot study, the feasibility and safety of tacrolimus monotherapy in immunologically low-risk kidney transplant recipients was evaluated [NTR4824, www.trialregister.nl]. Low immunological risk was defined as maximal 3 HLA mismatches and the absence of panel reactive antibodies. Six months after transplantation, recipients were randomized if eGFR >30 ml/min, proteinuria <50 mg protein/mmol creatinine, no biopsy-proven rejection after 3 months, and no lymphocyte depleting therapy given. Recipients were randomized to tacrolimus/mycophenolate mofetil (TAC/MMF) or to taper and discontinue MMF at month 9 (TACmono). 79 of the 121 recipients were randomized to either TACmono (n = 38) or TAC/MMF (n = 41). Mean recipient age was 59 years and 59% received a living donor transplant. The median follow-up was 62 months. After randomization, 3 TACmono and 4 TAC/MMF recipients experienced a biopsy-proven rejection. At 5 years follow-up, patient survival was 84% in TACmono versus 76% in TAC/MMF with death-censored graft survival of 97% for both groups and no differences in eGFR and proteinuria. Eleven TACmono recipients had an infectious episode versus 22 TAC/MMF recipients (p < 0.03). Donor-specific anti-HLA antibodies were not detected during follow-up in both groups. Tacrolimus monotherapy in selected immunologically low-risk kidney transplant recipients appears safe and reduces the number of infections.
Keywords: immunosuppression reduction; infection; kidney transplantation; mycophenolate mofetil; rejection; tacrolimus.
Copyright © 2022 de Weerd, Fatly, Boer-Verschragen, Kal-van Gestel, Roelen, Dieterich and Betjes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Salto-Alejandre S, Jimenez-Jorge S, Sabe N, Ramos-Martinez A, Linares L, Valerio M, et al. Risk Factors for Unfavorable Outcome and Impact of Early post-transplant Infection in Solid Organ Recipients with COVID-19: A Prospective Multicenter Cohort Study. PLoS One (2021) 16(4):e0250796. 10.1371/journal.pone.0250796 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stumpf J, Siepmann T, Lindner T, Karger C, Schwobel J, Anders L, et al. Humoral and Cellular Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Renal Transplant versus Dialysis Patients: A Prospective, Multicenter Observational Study Using mRNA-1273 or BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine. Lancet Reg Health Eur (2021) 9:100178. 10.1016/j.lanepe.2021.100178 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

