Curcumin alleviates experimental colitis via a potential mechanism involving memory B cells and Bcl-6-Syk-BLNK signaling
- PMID: 36353208
- PMCID: PMC9639655
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i40.5865
Curcumin alleviates experimental colitis via a potential mechanism involving memory B cells and Bcl-6-Syk-BLNK signaling
Abstract
Background: Immune dysfunction is the crucial cause in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which is mainly related to lymphocytes (T or B cells, incl-uding memory B cells), mast cells, activated neutrophils, and macrophages. As the precursor of B cells, the activation of memory B cells can trigger and differentiate B cells to produce a giant variety of inducible B cells and tolerant B cells, whose dysfunction can easily lead to autoimmune diseases, including IBD.
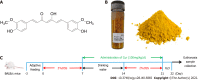
Aim: To investigate whether or not curcumin (Cur) can alleviate experimental colitis by regulating memory B cells and Bcl-6-Syk-BLNK signaling.
Methods: Colitis was induced in mice with a dextran sulphate sodium (DSS) solution in drinking water. Colitis mice were given Cur (100 mg/kg/d) orally for 14 con-secutive days. The colonic weight, colonic length, intestinal weight index, occult blood scores, and histological scores of mice were examined to evaluate the curative effect. The levels of memory B cells in peripheral blood of mice were measured by flow cytometry, and IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, IL-7A, and TNF-α expression in colonic tissue homogenates were analyzed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Western blot was used to measure the expression of Bcl-6, BLNK, Syk, and other signaling pathway related proteins.
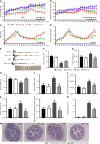
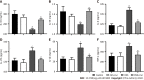
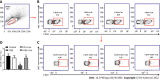
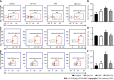
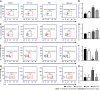
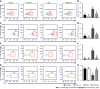
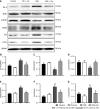
Results: After Cur treatment for 14 d, the body weight, colonic weight, colonic length, colonic weight index, and colonic pathological injury of mice with colitis were ameliorated. The secretion of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-7A was statistically decreased, while the IL-35 and IL-10 levels were considerably increased. Activation of memory B cell subsets in colitis mice was confirmed by a remarkable reduction in the expression of IgM, IgG, IgA, FCRL5, CD103, FasL, PD-1, CD38, and CXCR3 on the surface of CD19+ CD27+ B cells, while the number of CD19+ CD27+ IL-10+ and CD19+ CD27+ Tim-3+ B cells increased significantly. In addition, Cur significantly inhibited the protein levels of Syk, p-Syk, Bcl-6, and CIN85, and increased BLNK and p-BLNK expression in colitis mice.
Conclusion: Cur could effectively alleviate DSS-induced colitis in mice by regulating memory B cells and the Bcl-6-Syk-BLNK signaling pathway.
Keywords: BLNK; Bcl-6; Curcumin; Experimental colitis; Memory B cell.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: There are no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of curcumin on regulatory B cells in chronic colitis mice involving TLR/MyD88 signaling pathway.Phytother Res. 2023 Feb;37(2):731-742. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7656. Epub 2022 Oct 5. Phytother Res. 2023. PMID: 36196887
-
Curcumin alleviated dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by recovering memory Th/Tfh subset balance.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Sep 28;29(36):5226-5239. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i36.5226. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37901446 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of curcumin regulated memory Th7 cells in mice with DSS-induced colitis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Jan 3;145:113770. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113770. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39642569
-
Astragalus polysaccharides ameliorates experimental colitis by regulating memory B cells metabolism.Chem Biol Interact. 2024 May 1;394:110969. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2024.110969. Epub 2024 Mar 24. Chem Biol Interact. 2024. PMID: 38522565
-
Jianpi Qingchang decoction alleviates ulcerative colitis by inhibiting nuclear factor-κB activation.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Feb 21;23(7):1180-1188. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i7.1180. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28275298 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Gain-of-Function Variant in Spleen Tyrosine Kinase Regulates Macrophage Migration and Functions to Promote Intestinal Inflammation.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Nov 12;17:8713-8726. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S488901. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39559401 Free PMC article.
-
Mediating role of chiro-inositol metabolites on the effects of HLA-DR-expressing CD14 + monocytes in inflammatory bowel disease.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Jun 17;24(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03271-2. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38886630 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing Gastrointestinal Health: Curcumin's Efficacy and Nanopreparations.Molecules. 2024 Apr 7;29(7):1659. doi: 10.3390/molecules29071659. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38611938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitior of Bcl6 by FX1 protects DSS induced colitis mice through anti-inflammatory effects.Front Immunol. 2025 May 9;16:1558845. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1558845. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40416976 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Application of Chinese Herbal Compounds and Formulae in Intestinal Inflammation in Humans and Animals.Molecules. 2023 Sep 26;28(19):6811. doi: 10.3390/molecules28196811. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37836654 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mantzorou M, Pavlidou E, Vasios G, Tsagalioti E, Giaginis C. Effects of curcumin consumption on human chronic diseases: A narrative review of the most recent clinical data. Phytother Res. 2018;32:957–975. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

