Difficult-to-treat rheumatoid arthritis: Current concept and unsolved problems
- PMID: 36353219
- PMCID: PMC9637686
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1049875
Difficult-to-treat rheumatoid arthritis: Current concept and unsolved problems
Abstract
Over the past several decades, the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has advanced significantly, and clinical, structural, and functional remission are achievable therapeutic goals. However, a substantial number of patients show resistance to multiple drugs. In particular, patients whose disease activity cannot be controlled despite the use of two or more biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) or targeted synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARDs) with different mechanisms of action (MOA) have recently been referred to as having difficult-to-treat RA (D2T RA). D2T RA is a heterogeneous and multifactorial disease state, and the major problems are uncontrolled disease activity and decreased quality of life, as well as the economic burden due to frequent healthcare utilization and multiple admissions. Since the concept of D2T RA is relatively new and publication regarding D2T RA is limited, the mechanism underlying DMARD inefficacy and which factors form a "difficult-to-treat" state in such patients are not yet fully understood. It is also possible that factors contributing to D2T RA may differ by patient, sex, country, and race. The present Mini Review introduces the current concept and unsolved problems of D2T RA, including the definition, prevalence, and factors contributing to D2T RA. We then discuss the management and therapeutic strategies for D2T RA. Finally, we explore a clinical approach to prevent patients from developing D2T RA.
Keywords: difficult-to-treat; disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs; drug resistance; methotrexate; pulmonary involvement.
Copyright © 2022 Watanabe, Okano, Gon, Yoshida, Fukumoto, Yamada and Hashimoto.
Conflict of interest statement
Author RW received research grant and/or speaker’s fee from AbbVie and Eli Lilly. Author TO received research grant and/or speaker’s fee from Abbvie, Asahi Kasei, Chugai, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis Pharma and Tanabe Mitsubishi. Author MH received research grants and/or speaker fee from Abbvie, Asahi Kasei, Astellas, Ayumi, Brystol Meyers, Chugai, EA Pharma, Eisai, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Nihon Shinyaku, Novartis Pharma, Tanabe Mitsubishi. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

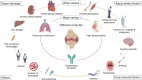
References
-
- Smolen JS, Landewe RBM, Bijlsma JWJ, Burmester GR, Dougados M, Kerschbaumer A, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann Rheum Dis. (2020) 79:685–99. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216655 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

