Identification of the effect and mechanism of Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder against colorectal cancer using network pharmacology and experimental validation
- PMID: 36353478
- PMCID: PMC9637639
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.929836
Identification of the effect and mechanism of Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder against colorectal cancer using network pharmacology and experimental validation
Abstract
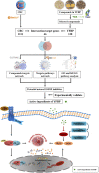
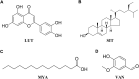
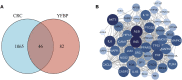
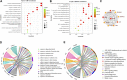
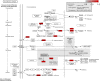
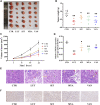
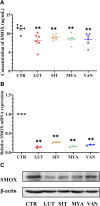
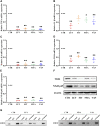
Background: Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder (YFBP) is a traditional Chinese medicine used to treat colorectal cancer, although its bioactivity and mechanisms of action have not been studied in depth yet. The study intended to identify the potential targets and signaling pathways affected by YFBP during the treatment of colorectal cancer through pharmacological network analysis and to further analyze its chemical compositions and molecular mechanisms of action. Methods: The Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology (TCMSP), Traditional Chinese Medicine Integrated Database (TCMID), HitPredict (HIT), and Search Tool for Interactions of Chemicals (STITCH) databases were used to screen the bioactive components and promising targets of YFBP. Targets related to colorectal cancer were retrieved from the GeneCards and Gene Ontology databases. Cytoscape software was used to construct the "herb-active ingredient-target" network. The STRING database was used to construct and analyze protein-protein interactions (PPIs). Afterward, the R packages clusterProfiler and Cytoscape Hub plug-in were used to perform Gene Ontology (GO) functional and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses of target genes. The results of the network pharmacological analysis were also experimentally validated. Results: In total, 33 active components and 128 target genes were screened. Among them, 46 target genes were considered potential therapeutic targets that crossed the CRC target genes. The network pharmacology analysis showed that the active components of YFBP were correlated positively with CRC inflammatory target genes such as TLR4, TNF, and IL-6. The inflammation-related signaling pathways affected by the active components included the TNF-α, interleukin-17, and toll-like receptor signaling pathways. The active ingredients of YFBP, such as luteolin, β-sitosterol, myristic acid, and vanillin, may exert anti-tumor effects by downregulating SMOX expression via anti-inflammatory signaling and regulation of the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Conclusion: In the present study, the potential active components, potential targets, and key biological pathways involved in the YFBP treatment of CRC were determined, providing a theoretical foundation for further anti-tumor research.
Keywords: SMOX; Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder; colorectal cancer; inflammatory; network pharmacology.
Copyright © 2022 Xiang, Geng, Zhang, Ji, Zou, Chen and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Exploring the mechanism of action of Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder in colorectal cancer based on network pharmacology and molecular docking studies.Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2023 Oct;39(2):1107-1127. doi: 10.1080/02648725.2023.2167765. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2023. PMID: 36735641 Review.
-
Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang Powder Alleviates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Rats via Inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling Pathway to Repair the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier, and Modulating Intestinal Microbiota.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023 Jan 14;2023:3071610. doi: 10.1155/2023/3071610. eCollection 2023. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023. PMID: 36691639 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology and molecular docking study on the mechanism of colorectal cancer treatment using Xiao-Chai-Hu-Tang.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 14;16(6):e0252508. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252508. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34125845 Free PMC article.
-
A network pharmacology-based investigation on the bioactive ingredients and molecular mechanisms of Gelsemium elegans Benth against colorectal cancer.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 Mar 20;21(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03273-7. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021. PMID: 33743701 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment of colorectal cancer by traditional Chinese medicine: prevention and treatment mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 9;15:1377592. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1377592. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38783955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Natural Products from Herbal Medicine in TLR4 Signaling for Colorectal Cancer Treatment.Molecules. 2024 Jun 7;29(12):2727. doi: 10.3390/molecules29122727. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38930793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Yi Gong San inhibits tumor immune escape by sensitizing colorectal cancer stem cells via the NF-κB pathway.Hereditas. 2025 Apr 17;162(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s41065-025-00412-9. Hereditas. 2025. PMID: 40247422 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated network pharmacology and metabolomics to reveal the mechanism of Pinellia ternata inhibiting non-small cell lung cancer cells.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024 Jul 11;24(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s12906-024-04574-3. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024. PMID: 38992647 Free PMC article.
-
PSKH1 affects proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells via the p38/MAPK signaling pathway.Oncol Lett. 2023 Feb 28;25(4):144. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.13730. eCollection 2023 Apr. Oncol Lett. 2023. PMID: 36936027 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

