Catalpol ameliorates CFA-induced inflammatory pain by targeting spinal cord and peripheral inflammation
- PMID: 36353492
- PMCID: PMC9637921
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1010483
Catalpol ameliorates CFA-induced inflammatory pain by targeting spinal cord and peripheral inflammation
Abstract
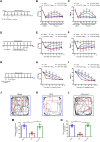
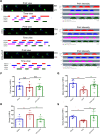
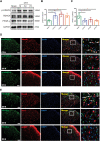
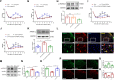
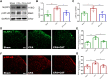
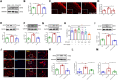
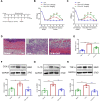
Chronic, inflammatory pain is an international health concern that severely diminishes individuals' quality of life. Catalpol is an iridoid glycoside derived from the roots of Rehmannia glutinosa that possesses anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuroprotective properties for the treating multiple kinds of disorders. Nevertheless, catalpol's impacts on inflammatory pain and its potential methods of action are still unclear. The purpose of this investigation is to determine the mechanism of catalpol to reduce the inflammatory pain behaviors in a rat model with complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA). Catwalk, Von-Frey, and open field testing were performed for behavioral assessment. Western blot analysis and real-time quantitative PCR (RT-PCR) were employed to identify variations in molecular expression, while immunofluorescence was utilized to identify cellular localization. Catalpol effectively reduced CFA-induced mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia when injected intrathecally. Moreover, catalpol can regulate the HDAC4/PPAR-γ-signaling pathway in CFA rat spinal cord neurons. Meanwhile catalpol significantly decreased the expression of the NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammatory axis in the spinal cord of CFA rats. In addition, both in vivo and in vitro research revealed that catalpol treatment inhibited astrocyte activation and increase inflammatory factor expression. Interestingly, we also found that catalpol could alleviate peripheral pain by inhibiting tissue inflammation. Taken together, the findings declared that catalpol may inhibit inflammatory pain in CFA rats by targeting spinal cord and peripheral inflammation.
Keywords: HDAC4/PPAR-γ -signaling pathway; NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammatory axis; astrocyte activation; catalpol; inflammatory pain; peripheral pain.
Copyright © 2022 Zhao, Fu, Ni, Xu, Xu, He, Ni, Wang, Kuang, Tang, Shou and Yao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trifluoro-icaritin alleviates chronic inflammatory pain through α7nAChR-mediated suppression of HMGB1/NF-κB signaling in the spinal cord of rats.Brain Res Bull. 2022 Jun 1;183:13-26. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.02.014. Epub 2022 Feb 22. Brain Res Bull. 2022. PMID: 35202753
-
Curcumin relieves CFA-induced inflammatory pain by inhibiting the AP-1/c-Jun-CCL2-CCR2 pathway in the spinal dorsal horn.Mol Pain. 2025 Jan-Dec;21:17448069251323668. doi: 10.1177/17448069251323668. Mol Pain. 2025. PMID: 39950445 Free PMC article.
-
Probucol Ameliorates Complete Freund's Adjuvant-Induced Hyperalgesia by Targeting Peripheral and Spinal Cord Inflammation.Inflammation. 2019 Aug;42(4):1474-1490. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01011-3. Inflammation. 2019. PMID: 31011926
-
Protective effects of catalpol on cardio-cerebrovascular diseases: A comprehensive review.J Pharm Anal. 2023 Oct;13(10):1089-1101. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2023.06.010. Epub 2023 Jun 21. J Pharm Anal. 2023. PMID: 38024856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular and Biochemical Pathways of Catalpol in Alleviating Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 20;11(2):323. doi: 10.3390/biom11020323. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33672590 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological Evaluation and In-Silico Study of Sabinene as a Potential Anti-Alzheimer's Drug in AlCl3-Induced Rat Model via BACE-1 and GSK3β Modulation.Neurochem Res. 2025 Aug 25;50(5):278. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04523-7. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40853403
-
Quantum Health Accelerator® Ameliorates CFA-Induced Animal Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Investigating the Role of Immunomodulatory and Anti-Oxidative Effects.Brain Sci. 2025 Feb 23;15(3):232. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15030232. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40149754 Free PMC article.
-
Translational evaluation of gait behavior in rodent models of arthritic disorders with the CatWalk device - a narrative review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Oct 6;10:1255215. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1255215. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37869169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRPM8's Role in the Shift Between Opioid and Cannabinoid Pathways in Electroacupuncture for Inflammatory Pain in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 3;25(23):13000. doi: 10.3390/ijms252313000. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684707 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of HDAC2-mediated kcnq2/kcnq3 genes transcription repression activated by EREG/EGFR-ERK-Runx1 signaling in bone cancer pain.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Aug 27;22(1):416. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01797-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39192337 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed O., Fahim H., Mahmoud A., Eman Ahmed E. A. (2018). Bee venom and hesperidin effectively mitigate complete Freund's adjuvant-induced arthritis via immunomodulation and enhancement of antioxidant defense system. Arch. Rheumatol. 33 (2), 198–212. 10.5606/ArchRheumatol.2018.6519 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

