The diagnostic significance of blood-derived circRNAs in NSCLC: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36353543
- PMCID: PMC9638072
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.987704
The diagnostic significance of blood-derived circRNAs in NSCLC: Systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Using blood-derived circular RNAs (circRNAs) may be an efficient tool for noninvasive fluid biopsy in diagnosing non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, no relevant systemic meta-analysis has been conducted so far to support the diagnostic value of using blood-derived circRNAs in NSCLC clinically. The aim of this study is to clarify the issue through a meta-analysis.
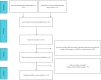
Methods: A systematic search strategy was used to search relevant literature in the databases of PubMed, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library from 2017 to 2022. The relationship between the diagnostic accuracy of circRNAs and NSCLC was analyzed. For the purpose of evaluating the quality of the literature, Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2 (QUADAS-2) was used. Statistical analyses were assessed using Stata software (version 17.0) and META-DISC (version 1.4).
Results: The meta-analysis included 1,093 patients with NSCLC and 959 controls. Results are as follows: pooled sensitivity, 0.78 (95% CI = 0.71-0.83, I2 = 71.86); pooled specificity, 0.76 (95% CI = 0.70-0.82, I2 = 70.12); pooled positive likelihood ratio (PLR), 3.3 (95% CI = 2.6-4.2, I2 = 37.56); pooled negative likelihood ratio (NLR), 0.29 (95% CI = 0.23-0.37, I2 = 64.67); diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), 11.42 (95% CI = 7.88-16.56, I2 = 99.05); area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), 0.84 (95% CI = 0.80-0.87). Based on the subgroup analysis, it appears that the heterogeneity is primarily caused by the NSCLC subgroup.
Conclusion: circRNAs are highly useful diagnostic biomarkers for NSCLC in China. Further prospective studies on the diagnostic value of circRNAs should be conducted in multiple countries.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD42022323804.
Keywords: NSCLC; blood-derived; circRNAs; diagnosis; oncology.
Copyright © 2022 Yu, Liu, Miao, Zhang, Sheyhidin and Ainiwaer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Long noncoding RNAs and circular RNAs as potential diagnostic biomarkers of inflammatory bowel diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 8;15:1362437. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1362437. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38524131 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Value of CircRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: a Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 8;11:693284. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.693284. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34307158 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and diagnostic value of circRNA expression in prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 7;12:945143. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.945143. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36419885 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA panels as diagnostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 7;9:915226. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.915226. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36419785 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of circRNAs in the Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 19;8:766208. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.766208. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34869475 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Lung adenocarcinoma size as a predictor of distant metastasis: A CT scan-based measurement.Narra J. 2024 Aug;4(2):e1024. doi: 10.52225/narra.v4i2.1024. Epub 2024 Aug 31. Narra J. 2024. PMID: 39280288 Free PMC article.
-
Potentialities and critical issues of liquid biopsy in clinical practice: An umbrella review.Transl Oncol. 2025 Feb;52:102172. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102172. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39817953 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

