Immune cell-lipoprotein imbalance as a marker for early diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer metastasis
- PMID: 36353553
- PMCID: PMC9638068
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.942964
Immune cell-lipoprotein imbalance as a marker for early diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer metastasis
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Immune cell-lipoprotein imbalance as a marker for early diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer metastasis.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 15;12:1118042. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1118042. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36591456 Free PMC article.
Abstract
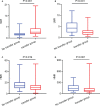
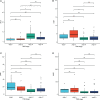
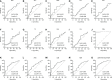
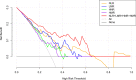
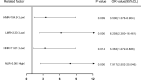
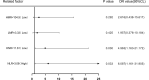
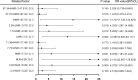
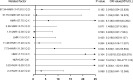
The underlying molecular mechanisms and evolutionary patterns of lung cancer metastasis remain unclear, resulting in a lack of effective indicators for early diagnosis of metastasis. We retrospectively analyzed 117 patients with primary non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) admitted to Tongji Hospital of Tongji University in 2021, of which 93 patients with tumor metastasis were set as the metastasis group. 24 patients without metastasis were set as the non-metastasis group. The differences of each index in the two groups of patients and the expression levels in different TNM stages were compared. This study intends to evaluate the diagnostic value and net clinical benefit of common blood-related indicators Neutrophil/lymphocyte (NLR), lymphocyte/monocyte (LMR), High density lipoprotein/neutrophil (HNR), High density lipoprotein/monocyte (HMR) and combined assays in NSCLC metastasis for the early diagnosis of patients with NSCLC metastasis. It was found that the level of NLR was higher in metastatic NSCLC than non-metastatic, but the level of LMR, HNR and HMR was lower. The levels of NLR, LMR, HNR and HMR in patients with different TNM stages showed that NLR levels increased with TNM stage, while LMR, HNR and HMR levels decreased. The threshold probability range of the 4 combined tests was greater and the overall clinical benefit rate was higher compared to the individual tests. Our findings suggest that NLR, LMR, HNR and HMR have better diagnostic value for NSCLC metastasis. This study provides a clinical basis for investigating the mechanisms by which immune cells and lipid metabolism-related proteins remodel the microenvironment prior to NSCLC metastasis.
Keywords: HNR; LMR; NLR; NSCLC; diagnostic markers; risk assessment.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Wang, Wu, Tian, Yan, Yuan, Yao, Shang and Quan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rice SR, Saboury B, Houshmand S, Salavati A, Kalbasi A, Goodman CR, et al. Quantification of global lung inflammation using volumetric 18F-FDG PET/CT parameters in locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy: A comparison of photon and proton radiation therapy. Nucl Med Commun (2019) 40:618–25. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0000000000000997 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

