Case Report: A case of advanced duodenal adenocarcinoma in complete remission after chemotherapy combined with targeted therapy and radiotherapy
- PMID: 36353566
- PMCID: PMC9638098
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.968110
Case Report: A case of advanced duodenal adenocarcinoma in complete remission after chemotherapy combined with targeted therapy and radiotherapy
Abstract
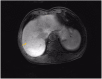
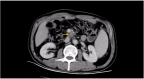
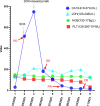
Duodenal adenocarcinoma (DA) is an extremely rare and highly aggressive malignant tumor of the digestive system. Due to the lack of specific clinical characteristics, it is easy to misdiagnosis and miss diagnosis, and the lack of specific consensus and recommendation for treatment, so it often refers to stomach cancer and colorectal cancer. Now, we report a case of a patient with advanced DA who achieved complete remission (CR) after undergoing chemoradiotherapy combined with targeted therapy. The patient was pathologically diagnosed with DA after radical surgery in October 2020, and he failed to undergo adjuvant chemotherapy on time due to the COVID-19 outbreak. The patient found multiple lymph node liver and abdominal metastases 6 months after the operation. Considering the progression of the disease, XELOX regimen (oxaliplatin + capecitabine) chemotherapy was given for 1 cycle. After 1 cycle of treatment, the tumor markers remained elevated; the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) was 5.03 ng/ml (0-5 ng/ml), and the carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) was 747.30 U/ml (0-37 U/ml). The patient also developed intolerable capecitabine-related treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs), namely, hand-foot syndrome. For the above reasons, capecitabine was replaced as S-1 at cycle 2, and the chemotherapy regimen became SOX (oxaliplatin + S-1); bevacizumab injection was also added to the SOX regimen, and it was further treated regularly for 7 cycles with the regimen of SOX plus bevacizumab. Liver metastases showed a continuous narrowing trend throughout the treatment period; tumor markers also showed a downward trend. Finally, the patient achieved complete remission (CR) at cycle 7. After completion of chemotherapy, radiotherapy was administered to the resistant metastatic lymph nodes present in the patient's abdominal cavity for a total of 10 times. However, the patient developed severe bone marrow suppression and obstructive jaundice during the course of radiotherapy and finally failed to complete the radiotherapy plan. Currently, the patient continued maintenance therapy with bevacizumab and S-1 and showed no recurrence or metastasis after review. In this case of advanced DA, we referred to both CRC and gastric cancer in the treatment regimen of the patient. At the same time, targeted drugs and radiotherapy were also added to the basis of chemotherapy, which has no clear consensus recommendation or case for reference in the treatment of advanced DA. Thankfully, the patient's disease was controlled and remained stable after treatment with this regimen. Therefore, for patients with advanced DA who lack standardized treatment regimens and guidelines, the combination of chemotherapy with targeted therapy and radiotherapy may be one of the effective treatment modalities.
Keywords: advanced stage; case report; chemotherapy; duodenal adenocarcinoma; radiotherapy; targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Lei, Wang, Yang and Lou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
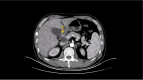
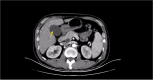
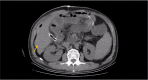
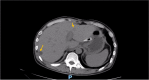

References
-
- Noya G, Bianco F, Dettori G, Antona C, Biglioli P. Primary adenocarcinoma of the 3d duodenal segment. Minerva Chir (1981) 36(11):765–70. - PubMed
-
- Thiruvengadam SS, Lopez R, O'malley M, LaGuardia L, Church JM, Kalady M, et al. Spigelman stage IV duodenal polyposis does not precede most duodenal cancer cases in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Gastrointest Endosc (2019) 89(2):345–54 e2. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2018.07.033 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

