Beneficial effects of natural flavonoids on neuroinflammation
- PMID: 36353622
- PMCID: PMC9638012
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1006434
Beneficial effects of natural flavonoids on neuroinflammation
Abstract
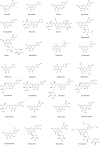
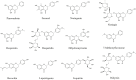
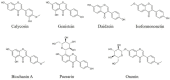
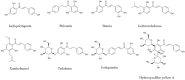
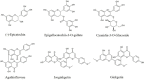
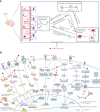
Neuroinflammation is the fundamental immune response against multiple factors in the central nervous system and is characterized by the production of inflammatory mediators, activated microglia and astrocytes, and the recruitment of innate and adaptive immune cells to inflammatory sites, that contributes to the pathological process of related brain diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, depression, and stroke. Flavonoids, as a species of important natural compounds, have been widely revealed to alleviate neuroinflammation by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory mediators, elevating the secretion of anti-inflammatory factors, and modulating the polarization of microglia and astrocyte, mainly via suppressing the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome, as well as NF-κB, MAPK, and JAK/STAT pathways, promoting Nrf2, AMPK, BDNF/CREB, Wnt/β-Catenin, PI3k/Akt signals and SIRT1-mediated HMGB1 deacetylation. This review will provide the latest and comprehensive knowledge on the therapeutic benefits and mechanisms of natural flavonoids in neuroinflammation, and the natural flavonoids might be developed into food supplements or lead compounds for neuroinflammation-associated brain disorders.
Keywords: astrocytes; brain disorders; microglia; natural flavonoids; neuroinflammation.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Peng, Xing, Chen, Peng and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The interaction of lipocalin-2 and astrocytes in neuroinflammation: mechanisms and therapeutic application.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 12;15:1358719. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1358719. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38533497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid attenuates the inflammatory response by modulating microglia polarization through SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of the HMGB1/NF-κB pathway following experimental traumatic brain injury.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Apr 20;15(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1151-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29678169 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoids and ischemic stroke-induced neuroinflammation: Focus on the glial cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Jan;170:115847. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115847. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38016362 Review.
-
Anti-neuroinflammatory effect of Sophoraflavanone G from Sophora alopecuroides in LPS-activated BV2 microglia by MAPK, JAK/STAT and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways.Phytomedicine. 2016 Dec 1;23(13):1629-1637. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2016.10.007. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Phytomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27823627
-
Flavonoids in the regulation of microglial-mediated neuroinflammation; focus on fisetin, rutin, and quercetin.Exp Cell Res. 2025 Apr 15;447(2):114537. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2025.114537. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Exp Cell Res. 2025. PMID: 40147710 Review.
Cited by
-
The Flavonoid Rich Black Currant (Ribes nigrum) Ethanolic Gemmotherapy Extract Elicits Neuroprotective Effect by Preventing Microglial Body Swelling in Hippocampus and Reduces Serum TNF-α Level: Pilot Study.Molecules. 2023 Apr 19;28(8):3571. doi: 10.3390/molecules28083571. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37110805 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Cocoa Flavanols Do Not Alter Brain Excitability in Young Healthy Adults.Nutrients. 2024 Mar 27;16(7):969. doi: 10.3390/nu16070969. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38613003 Free PMC article.
-
Natural drug delivery systems for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Feb 10;52(1):217. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10286-9. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39928236 Review.
-
Food and medicine homology: a potential nutritional intervention strategy for post-acute COVID-19 syndrome.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 3;16:1588037. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1588037. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40678729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT1 activation by 2,3,5,6-tetramethylpyrazine alleviates neuroinflammation via inhibiting M1 microglia polarization.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 4;14:1206513. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1206513. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37600790 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

