SpiDec: Computing binodals and interfacial tension of biomolecular condensates from simulations of spinodal decomposition
- PMID: 36353733
- PMCID: PMC9637972
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1021939
SpiDec: Computing binodals and interfacial tension of biomolecular condensates from simulations of spinodal decomposition
Abstract
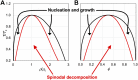
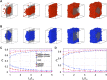
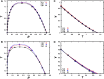
Phase separation of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) is a phenomenon associated with many essential cellular processes, but a robust method to compute the binodal from molecular dynamics simulations of IDPs modeled at the all-atom level in explicit solvent is still elusive, due to the difficulty in preparing a suitable initial dense configuration and in achieving phase equilibration. Here we present SpiDec as such a method, based on spontaneous phase separation via spinodal decomposition that produces a dense slab when the system is initiated at a homogeneous, low density. After illustrating the method on four model systems, we apply SpiDec to a tetrapeptide modeled at the all-atom level and solvated in TIP3P water. The concentrations in the dense and dilute phases agree qualitatively with experimental results and point to binodals as a sensitive property for force-field parameterization. SpiDec may prove useful for the accurate determination of the phase equilibrium of IDPs.
Keywords: binodal; biomolecular condensates; interfacial tension; phase equilibrium; phase separation; spinodal decomposition.
Copyright © 2022 Mazarakos, Prasad and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Berendsen H. J. C., Postma J. P. M., Gunsteren W. F. v., DiNola A., Haak J. R. (1984). Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 81, 3684–3690. 10.1063/1.448118 - DOI
-
- Binder K., Block B. J., Virnau P., Tröster A. (2012). Beyond the van der Waals loop: What can Be learned from simulating Lennard-Jones fluids inside the region of phase coexistence. Am. J. Phys. 80, 1099–1109. 10.1119/1.4754020 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

