The stationary phase-specific sRNA FimR2 is a multifunctional regulator of bacterial motility, biofilm formation and virulence
- PMID: 36354005
- PMCID: PMC9723502
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkac1025
The stationary phase-specific sRNA FimR2 is a multifunctional regulator of bacterial motility, biofilm formation and virulence
Abstract
Bacterial pathogens employ a plethora of virulence factors for host invasion, and their use is tightly regulated to maximize infection efficiency and manage resources in a nutrient-limited environment. Here we show that during Escherichia coli stationary phase the 3' UTR-derived small non-coding RNA FimR2 regulates fimbrial and flagellar biosynthesis at the post-transcriptional level, leading to biofilm formation as the dominant mode of survival under conditions of nutrient depletion. FimR2 interacts with the translational regulator CsrA, antagonizing its functions and firmly tightening control over motility and biofilm formation. Generated through RNase E cleavage, FimR2 regulates stationary phase biology by fine-tuning target mRNA levels independently of the chaperones Hfq and ProQ. The Salmonella enterica orthologue of FimR2 induces effector protein secretion by the type III secretion system and stimulates infection, thus linking the sRNA to virulence. This work reveals the importance of bacterial sRNAs in modulating various aspects of bacterial physiology including stationary phase and virulence.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

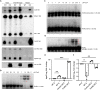
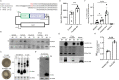
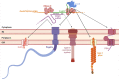
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification of Hfq-regulated small RNAs in the fire blight pathogen Erwinia amylovora discovered small RNAs with virulence regulatory function.BMC Genomics. 2014 May 31;15(1):414. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-414. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24885615 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic interactions between the RNA chaperone Hfq, small regulatory RNAs, and mRNAs in live bacterial cells.Elife. 2021 Feb 22;10:e64207. doi: 10.7554/eLife.64207. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33616037 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and RNA-binding properties of the bacterial LSm protein Hfq.RNA Biol. 2013 Apr;10(4):610-8. doi: 10.4161/rna.24201. Epub 2013 Mar 27. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23535768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A pathogen-specific sRNA influences enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli fitness and virulence in part by direct interaction with the transcript encoding the ethanolamine utilization regulatory factor EutR.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Nov 8;49(19):10988-11004. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab863. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34591974 Free PMC article.
-
Global regulation by the small RNA-binding protein CsrA and the non-coding RNA molecule CsrB.Mol Microbiol. 1998 Sep;29(6):1321-30. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.01021.x. Mol Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 9781871 Review.
Cited by
-
Prokaryotic ncRNAs: Master regulators of gene expression.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022 Oct 17;3:100136. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100136. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 36568271 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the regulatory role of bacterial sncRNA and its extracellular delivery via OMVs.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Dec;108(1):29. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12855-z. Epub 2023 Dec 30. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38159117 Review.
-
A phosphate starvation induced small RNA promotes Bacillus biofilm formation.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024 Oct 29;10(1):115. doi: 10.1038/s41522-024-00586-6. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024. PMID: 39472585 Free PMC article.
-
sRNA113 regulates Pseudomonas plecoglossicida motility to affect immune response against infection in pearl gentian grouper.Zool Res. 2025 Jan 18;46(1):152-164. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2024.333. Zool Res. 2025. PMID: 39846193 Free PMC article.
-
A trans-acting sRNA SaaS targeting hilD, cheA and csgA to inhibit biofilm formation of S. Enteritidis.J Adv Res. 2025 May;71:127-139. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.06.008. Epub 2024 Jun 7. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 38852803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaper J.B., Nataro J.P., Mobley H.L.T.. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004; 2:123–140. - PubMed
-
- Martínez L.C., Yakhnin H., Camacho M.I., Georgellis D., Babitzke P., Puente J.L., Bustamante V.H.. Integration of a complex regulatory cascade involving the SirA/BarA and csr global regulatory systems that controls expression of the salmonella SPI-1 and SPI-2 virulence regulons through hilD. Mol. Microbiol. 2011; 80:1637–1656. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

