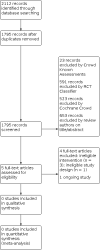
Pharmacological interventions for pain and sedation management in newborn infants undergoing therapeutic hypothermia
- PMID: 36354070
- PMCID: PMC9647594
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD015023.pub2
Pharmacological interventions for pain and sedation management in newborn infants undergoing therapeutic hypothermia
Abstract
Background: Newborn infants affected by hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) undergo therapeutic hypothermia. As this treatment seems to be associated with pain, and intensive and invasive care is needed, pharmacological interventions are often used. Moreover, painful procedures in the newborn period can affect pain responses later in life, impair brain development, and possibly have a long-term negative impact on neurodevelopment and quality of life.
Objectives: To determine the effects of pharmacological interventions for pain and sedation management in newborn infants undergoing therapeutic hypothermia. Primary outcomes were analgesia and sedation, and all-cause mortality to discharge.
Search methods: We searched CENTRAL, PubMed, CINAHL (Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature), and the trial register ISRCTN in August 2021. We also checked the reference lists of relevant articles to identify additional studies.
Selection criteria: We included randomized controlled trials (RCT), quasi-RCTs and cluster-randomized trials comparing drugs used for the management of pain or sedation, or both, during therapeutic hypothermia: any opioids (e.g. morphine, fentanyl), alpha-2 agonists (e.g. clonidine, dexmedetomidine), N-Methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist (e.g. ketamine), other analgesics (e.g. paracetamol), and sedatives (e.g. benzodiazepines such as midazolam) versus another drug, placebo, no intervention, or non-pharmacological interventions. Primary outcomes were analgesia and sedation, and all-cause mortality to discharge.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed studies identified by the search strategy for inclusion. We planned to use the GRADE approach to assess the certainty of evidence. We planned to assess the methodological quality of included trials using Cochrane Effective Practice and Organisation of Care Group (EPOC) criteria (assessing randomization, blinding, loss to follow-up, and handling of outcome data). We planned to evaluate treatment effects using a fixed-effect model with risk ratio (RR) for categorical data and mean, standard deviation (SD), and mean difference (MD) for continuous data. MAIN RESULTS: We did not find any completed studies for inclusion. Amongst the four excluded studies, topiramate and atropine were used in two and one trial, respectively; one study used dexmedetomidine and was initially reported in 2019 to be a randomized trial. However, it was an observational study (correction in 2021). We identified one ongoing study comparing dexmedetomidine to morphine.
Authors' conclusions: We found no studies that met our inclusion criteria and hence there is no evidence to recommend or refute the use of pharmacological interventions for pain and sedation management in newborn infants undergoing therapeutic hypothermia.
Copyright © 2022 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
PB has no interests to declare.
MB has no interests to declare.
GS has no interests to declare.
YTB has no interests to declare.
EO has no interests to declare.
Update of
References
References to studies excluded from this review
Filippi 2018 {published data only}
-
- Filippi L, Fiorini P, Catarzi S, Berti E, Padrini L, Landucci E, et al. Safety and efficacy of topiramate in neonates with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy treated with hypothermia (NeoNATI): a feasibility study. Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine 2018;31(8):973-80. [DOI: 10.1080/14767058.2017.1304536] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Gill 2014 {published data only}
-
- Gill H, Thoresen M, Smit E, Davis J, Liu X, Dingley J, et al. Sedation management during therapeutic hypothermia for neonatal encephalopathy: atropine premedication for endotracheal intubation causes a prolonged increase in heart rate. Resuscitation 2014;85(10):1394-8. [DOI: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2014.07.002] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Nuñez‐Ramiro 2019 {published data only}
-
- Nuñez-Ramiro A, Benavente-Fernández I, Valverde E, Cordeiro M, Blanco D, Boix H, et al, on behalf of the Hypotop Study Group. Topiramate plus cooling for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a randomized, controlled, multicenter, double-blinded trial. Neonatology 2019;116(1):76-84. [DOI: 10.1159/000499084] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Surkov 2019 {published data only}
-
- Surkov D. CORRECTION: Using of dexmedetomidine in term neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy [Застосування дексмедетомідину в доношених новонароджених з гіпоксично-ішемічною енцефалопатією]. Medical Perspectives-Medicni Perspektivi [Internet] 2021;26(3):230. [DOI: 10.26641/2307-0404.2021.3.242347] [journals.uran.ua/index.php/2307-0404/article/view/242347] - DOI
-
- Surkov D. Using of dexmedetomidine in term neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Intensive care medicine experimental 2018;6(Suppl 2):0486.
-
- Surkov D. Using of dexmedetomidine in term neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy [Застосування дексмедетомідину в доношених новонароджених з гіпоксично-ішемічною енцефалопатією]. Medical Perspectives-Medicni Perspektivi 2019;2(24):332019. [DOI: 10.26641/2307-0404.2019.2.170123] - DOI
References to ongoing studies
NCT04772222 {published data only}
-
- Dexmedetomidine use in infants undergoing cooling due to neonatal encephalopathy (DICE Trial). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04772222 (first received 26 February 2021).
Additional references
Ainsworth 2015
-
- Ainsworth SB. Effects of therapeutic hypothermia on medications. In: Neonatal formulary 7: drug use in pregnancy and the first year of life. 7th edition. West Sussex: John Wiley & Sons, 2015. [ISBN: 978-1-118-81959-3]
Allegaert 2017
Axelin 2013
Balda 2019
-
- Balda RC, Guinsburg R. Evaluation and treatment of pain in the neonatal period [Avaliação e tratamento da dor no período neonatal]. Revista Pediátrica - Publicação Oficial da Sociedade Brasileira de Pediatria 2019;9(1):43-52. [DOI: 10.25060/residpediatr-2019.v9n1-13] - DOI
Bayley 1993
-
- Bayley N. Bayley scales of infant development–II. San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation, 1993.
Bayley 2005
-
- Bayley N. Bayley scales of infant and toddler development. 3rd edition. San Antonio, TX: Harcourt Assessment, 2005.
Bellù 2021
Berube 2020
Bruschettini 2020
-
- Bruschettini M, Romantsik O, Moreira A, Ley D, Thébaud B. Stem cell-based interventions for the prevention of morbidity and mortality following hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy in newborn infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2020, Issue 8. Art. No: CD013202. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013202.pub2] [PMID: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Bruschettini 2022
-
- Bruschettini M, Olsson E, Persad E, Garratt A, Roger S. Clinical rating scales for assessing pain in newborn infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2022, Issue 3. Art. No: MR000064. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.MR000064] - DOI
Carter 2017
Chau 2019
COMFORTNeo 2016
-
- Dijk M. Comfort assessment NeoScale version 5; 2016. Available at www.comfortassessment.nl/web/files/8414/7936/9137/COMFORT_Neo_scale___fi....
Craig 2020
Debillon 2001
de Haan 2012
-
- Haan T, Bijleveld Y, Lee J, Groenendaal F, den Broek M, Rademaker C, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of medication in asphyxiated newborns during controlled hypothermia. The PharmaCool multicenter study. BMC Pediatrics 2012;22(12):45. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2431-12-45] [PMID: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Donato 2020
EPOC 2017
-
- Cochrane Effective Practice and Organisation of Care (EPOC). EPOC resources for review authors, 2017. Available at epoc.cochrane.org/resources/epoc-resources-review-authors.
Ergenekon 2016
-
- Ergenekon E. Therapeutic hypothermia in neonatal intensive care unit: challenges and practical points. Journal of Clinical Neonatology 2016;5(1):8-17. [DOI: 10.4103/2249-4847.173271] - DOI
Favié 2019
-
- Favié LM, Groenendaal F, den Broek MP, Rademaker CM, Haan TR, Straaten HL, et al, on behalf of the PharmaCool study group. Phenobarbital, midazolam pharmacokinetics, effectiveness, and drug-drug interaction in asphyxiated neonates undergoing therapeutic hypothermia. Neonatology 2019;116(2):154-62. [DOI: 10.1159/000499330] [PMID: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Filippi 2011
Fisher 2005
-
- Fisher RS, Emde BW, Blume W, Elger C, Genton P, Lee P, et al. Epileptic seizures and epilepsy: definitions proposed by the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) and the International Bureau for Epilepsy (IBE). Epilepsia 2005;46(4):470-2. [DOI: 10.1111/j.0013-9580.2005.66104.x] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
-
- GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed 17 October 2021. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime). Available at gradepro.org.
Griffiths 1954
-
- Griffiths R. The abilities of babies: a study of mental measurement. London, UK: University of London Press, 1954.
Griffiths 1970
-
- Griffiths R. The abilities of young children: a comprehensive system of mental measurement for the first eight years. London, UK: Child Development Research Center, 1970.
Grunau 1986
Gunn 2017
Herrera 2018
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Altman DG, Sterne JA: on behalf of the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group and the Cochrane Bias Methods Group. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from training.cochrane.org/handbook/archive/v5.1/.
Higgins 2021a
-
- Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.2 (updated February 2021). Cochrane, 2021. Available from training.cochrane.org/handbook. - PMC - PubMed
Higgins 2021b
-
- Higgins JP, Eldridge S, Li T, editor(s). Chapter 23: Including variants on randomized trials. In: Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.2 (updated February 2021). Cochrane, 2021. Available from training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Hoffman 2013
Hong 2010
Hummel 2008
-
- Hummel P, Puchalski M, Creech SD, Weiss MG. Clinical reliability and validity of the N-PASS: neonatal pain, agitation and sedation scale with prolonged pain. Journal of Perinatology: Official Journal of the California Perinatal Association 2008;28(1):55-60. [DOI: 10.1038/sj.jp.7211861] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Ibrahim 2016
Jacobs 2013
Kinoshita 2021a
Kinoshita 2021b
Kinoshita 2021c
-
- Kinoshita M, Olsson E, Borys F, Bruschettini M. Opioids for procedural pain in neonates. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2021, Issue 12. Art. No: CD015056. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD015056] - DOI
Krechel 1995
Laptook 2016
Lee 2013
Lundqvist 2014
Mangat 2018
Marshall 2018
McCann 2012
McPherson 2020
Moher 2009
Ng 2017
Noel‐Storr 2020
-
- Noel-Storr AH, Dooley G, Wisniewski S, Glanville J, Thomas J, Cox S, et al. Cochrane centralised search service showed high sensitivity identifying randomised controlled trials: a retrospective analysis. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2020;127:142-50. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2020.08.008] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Noel‐Storr 2021
-
- Noel-Storr AH, Dooley G, Elliott J, Steele E, Shemilt I, Mavergames C, et al. An evaluation of Cochrane Crowd found that crowdsourcing produced accurate results in identifying randomised trials. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2021;133:130-39. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2021.01.006] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
O'Mara 2018
Ohlsson 2020
Olsson 2021
-
- Olsson E, Bruschettini M, Thernström Blomqvist Y, Bäcke P. IPSNUT - Interventions for the management of Pain and Sedation in Newborns undergoing Therapeutic hypothermia for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy - A systematic review. PROSPERO 2020 CRD42020205755. Available from: www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42020205755.
Pacifici 2014
-
- Pacifici GM. Clinical pharmacology of analgesics in infants and the pharmacologic management of pain in neonates. Medical Express 2014;1(1):105-15. [DOI: 10.5935/MedicalExpress.2014.03.03] - DOI
Pacifici 2016
Pauliah 2013
Peters 2003
Pillai Riddell 2015
Pirlotte 2019
Pressler 2021
-
- Pressler RM, Cilio MR, Mizrahi EM, Moshé SL, Nunes ML, Plouin P, et al. The ILAE classification of seizures and the epilepsies: modification for seizures in the neonate. Position paper by the ILAE Task Force on Neonatal Seizures. Epilepsia 2021;62(3):615-28. [DOI: 10.1111/epi.16815] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Review Manager 2020 [Computer program]
-
- Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.4. Copenhagen: The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020.
Romantsik 2017
Romantsik 2020
Saarenmaa 2001
Sarnat 1976
Schiller 2018
Schünemann 2013
-
- Schünemann H, Brożek J, Guyatt G, Oxman A, editor(s). Handbook for grading the quality of evidence and the strength of recommendations using the GRADE approach (updated October 2013). GRADE Working Group, 2013. Available from gdt.guidelinedevelopment.org/app/handbook/handbook.html.
Szakmar 2018
Thomas 2021
-
- Thomas J, McDonald S, Noel-Storr AH, Shemilt I, Elliott J, Mavergames C, et al. Machine learning reduces workload with minimal risk of missing studies: development and evaluation of an RCT classifier for Cochrane Reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2021;133:140-51. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2020.11.003vcvc] [PMID: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Tsuchida 2013
-
- Tsuchida TN, Wusthoff CJ, Shellhaas RA, Hahn CD, Sullivan JE, Nguyen S, et al, American Clinical Neurophysiology Society Critical Care Monitoring Committee. American Clinical Neurophysiology Society standardized EEG terminology and categorization for the description of continuous EEG monitoring in neonates: report of the American Clinical Neurophysiology Society Critical Care Monitoring Committee. Journal of Clinical Neurophysiology 2013;30(2):161-73. [DOI: 10.1097/WNP.0b013e3182872b24] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Üner 2019
van Dijk 2009
Walker 2017
Walker 2019
Wassink 2015
Wassink 2019
Williams 2020
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous