Transcriptomic and Functional Approaches Unveil the Role of tmRNA in Zinc Acetate Mediated Levofloxacin Sensitivity in Helicobacter pylori
- PMID: 36354329
- PMCID: PMC9769675
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01152-22
Transcriptomic and Functional Approaches Unveil the Role of tmRNA in Zinc Acetate Mediated Levofloxacin Sensitivity in Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
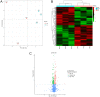
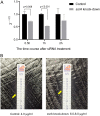
Rapid increase in resistance of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) has hindered antibiotics-based eradication efforts worldwide and raises the need for additional approaches. Here, we investigate the role of zinc-based compounds in inhibiting H. pylori growth and modulating antibiotic sensitivities, interrogate their downstream transcriptomic changes, and highlight the potential mechanism driving the observed effects. We showed that zinc acetate inhibited H. pylori growth and increased H. pylori sensitivity to levofloxacin. Transcriptomic profiling showed distinct gene expression patterns between zinc acetate treated groups versus controls. In particular, we independently replicated the association between zinc acetate treatment and increased ssrA expression. Knockdown of ssrA restored levofloxacin resistance to levels of the control group. In this study, we first demonstrated the role of zinc acetate in H. pylori growth and antibiotic sensitivities. Additionally, we explored the transcriptomic perturbations of zinc acetate followed by functional knockdown follow-up of differentially expressed ssrA, highlighting the role of tmRNA and trans-translation in H. pylori levofloxacin resistance. Our results provide alternative and complementary strategies for H. pylori treatment and shed light on the underlying mechanisms driving these effects. IMPORTANCE Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) eradication plays an important role in gastric cancer prevention, but the antimicrobial resistance of H. pylori is fast becoming a growing concern. In this study, we investigated the role of zinc acetate in inhibiting H. pylori growth and modulating antibiotic sensitivities in vitro. Additionally, we explored the transcriptomic perturbations of zinc acetate followed by functional knockdown follow-up of differentially expressed ssrA, highlighting the role of tmRNA and trans-translation in H. pylori levofloxacin resistance. Our results open up a new horizon for the treatment of antibiotic-resistant H. pylori.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; levofloxacin resistance; ssrA; transcriptomics; zinc acetate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

