An Experimental Framework for Developing Point-of-Need Biosensors: Connecting Bio-Layer Interferometry and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
- PMID: 36354449
- PMCID: PMC9688365
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12110938
An Experimental Framework for Developing Point-of-Need Biosensors: Connecting Bio-Layer Interferometry and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
Abstract
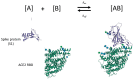
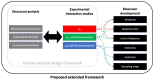
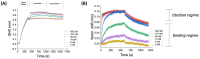
Biolayer interferometry (BLI) is a well-established laboratory technique for studying biomolecular interactions important for applications such as drug development. Currently, there are interesting opportunities for expanding the use of BLI in other fields, including the development of rapid diagnostic tools. To date, there are no detailed frameworks for implementing BLI in target-recognition studies that are pivotal for developing point-of-need biosensors. Here, we attempt to bridge these domains by providing a framework that connects output(s) of molecular interaction studies with key performance indicators used in the development of point-of-need biosensors. First, we briefly review the governing theory for protein-ligand interactions, and we then summarize the approach for real-time kinetic quantification using various techniques. The 2020 PRISMA guideline was used for all governing theory reviews and meta-analyses. Using the information from the meta-analysis, we introduce an experimental framework for connecting outcomes from BLI experiments (KD, kon, koff) with electrochemical (capacitive) biosensor design. As a first step in the development of a larger framework, we specifically focus on mapping BLI outcomes to five biosensor key performance indicators (sensitivity, selectivity, response time, hysteresis, operating range). The applicability of our framework was demonstrated in a study of case based on published literature related to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to show the development of a capacitive biosensor based on truncated angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as the receptor. The case study focuses on non-specific binding and selectivity as research goals. The proposed framework proved to be an important first step toward modeling/simulation efforts that map molecular interactions to sensor design.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; analytical sensing; binding kinetics; biosensor design; molecular affinity; protein–protein interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

