Novel Pumping Methods for Microfluidic Devices: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 36354465
- PMCID: PMC9688261
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12110956
Novel Pumping Methods for Microfluidic Devices: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
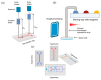
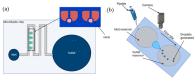
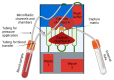
This review is an account of methods that use various strategies to control microfluidic flow control with high accuracy. The reviewed systems are divided into two large groups based on the way they create flow: passive systems (non-mechanical systems) and active (mechanical) systems. Each group is presented by a number of device fabrications. We try to explain the main principles of operation, and we list advantages and disadvantages of the presented systems. Mechanical systems are considered in more detail, as they are currently an area of increased interest due to their unique precision flow control and "multitasking". These systems are often applied as mini-laboratories, working autonomously without any additional operations, provided by humans, which is very important under complicated conditions. We also reviewed the integration of autonomous microfluidic systems with a smartphone or single-board computer when all data are retrieved and processed without using a personal computer. In addition, we discuss future trends and possible solutions for further development of this area of technology.
Keywords: active pumping methods; lab-on-a-chip; lab-on-a-disk; microfluidics; passive pumping methods; point-of-care devices.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

