Resorbable Membrane Pouch Technique for Single-Implant Placement in the Esthetic Zone: A Preliminary Technical Case Report
- PMID: 36354560
- PMCID: PMC9687625
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering9110649
Resorbable Membrane Pouch Technique for Single-Implant Placement in the Esthetic Zone: A Preliminary Technical Case Report
Abstract
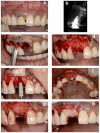
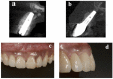
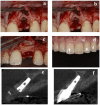
The conventional protocol for lateral guided bone regeneration (GBR) in esthetic areas requires the securing of resorbable collagen membranes using titanium cortical bone pins to immobilize bone grafts. These procedures are highly invasive and can increase patient morbidity and discomfort. Herein, we introduce a minimally invasive novel resorbable membrane pouch technique, wherein collagen membranes can be immobilized by securing them to the periosteum without the need of titanium pins. We describe 11 cases of single-immediate- or delayed-implant placement in the atrophic maxilla esthetic zone. All implants were successful and functional without pain or inflammation and with optimal soft-tissue health and esthetics. Radiographic evaluation with cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) and esthetic assessment using the pink esthetic score (PES) were performed. At the time of implant placement, the average augmented bone width was 2.8 ± 0.6 mm on CBCT analysis. In all cases, resorption of the augmented bone was confirmed with an average of -1.3 ± 0.8 mm. Soft-tissue outcomes were scored 1 year after permanent restoration. The PES score 1 year after treatment was 11.9 ± 1.4. The resorbable membrane pouch technique with immediate or delayed implant placement for buccal dehiscence in the esthetic area can be predictable and is minimally invasive.
Keywords: case report; connective-tissue graft; dental implant; resorbable membrane pouch techniques.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Chen S.T., Wilson T.G., Jr., Hämmerle C.H. Immediate or early placement of implants following tooth extraction: Review of biologic basis, clinical procedures, and outcomes. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants. 2004;19:12–25. - PubMed
-
- Zhou X., Yang J., Wu L., Tang X., Mou Y., Sun W., Hu Q., Xie S. Evaluation of the effect of implants placed in preserved sockets versus fresh sockets on tissue preservation and esthetics: A meta-analysis and systematic review. J. Evid. Based. Dent. Pract. 2019;19:101336. doi: 10.1016/j.jebdp.2019.05.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen S.T., Buser D. Clinical and esthetic outcomes of implants placed in postextraction sites. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants. 2009;24:186–217. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

