In Silico Identification of Promising New Pyrazole Derivative-Based Small Molecules for Modulating CRMP2, C-RAF, CYP17, VEGFR, C-KIT, and HDAC-Application towards Cancer Therapeutics
- PMID: 36354673
- PMCID: PMC9689108
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb44110361
In Silico Identification of Promising New Pyrazole Derivative-Based Small Molecules for Modulating CRMP2, C-RAF, CYP17, VEGFR, C-KIT, and HDAC-Application towards Cancer Therapeutics
Abstract
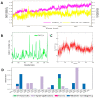
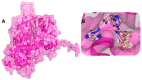
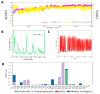
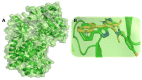
Despite continual efforts being made with multiple clinical studies and deploying cutting-edge diagnostic tools and technologies, the discovery of new cancer therapies remains of severe worldwide concern. Multiple drug resistance has also emerged in several cancer cell types, leaving them unresponsive to the many cancer treatments. Such a condition always prompts the development of next-generation cancer therapies that have a better chance of inhibiting selective target macromolecules with less toxicity. Therefore, in the present study, extensive computational approaches were implemented combining molecular docking and dynamic simulation studies for identifying potent pyrazole-based inhibitors or modulators for CRMP2, C-RAF, CYP17, c-KIT, VEGFR, and HDAC proteins. All of these proteins are in some way linked to the development of numerous forms of cancer, including breast, liver, prostate, kidney, and stomach cancers. In order to identify potential compounds, 63 in-house synthesized pyrazole-derivative compounds were docked with each selected protein. In addition, single or multiple standard drug compounds of each protein were also considered for docking analyses and their results used for comparison purposes. Afterward, based on the binding affinity and interaction profile of pyrazole compounds of each protein, potentially strong compounds were filtered out and further subjected to 1000 ns MD simulation analyses. Analyzing parameters such as RMSD, RMSF, RoG and protein-ligand contact maps were derived from trajectories of simulated protein-ligand complexes. All these parameters turned out to be satisfactory and within the acceptable range to support the structural integrity and interaction stability of the protein-ligand complexes in dynamic state. Comprehensive computational analyses suggested that a few identified pyrazole compounds, such as M33, M36, M72, and M76, could be potential inhibitors or modulators for HDAC, C-RAF, CYP72 and VEGFR proteins, respectively. Another pyrazole compound, M74, turned out to be a very promising dual inhibitor/modulator for CRMP2 and c-KIT proteins. However, more extensive study may be required for further optimization of the selected chemical framework of pyrazole derivatives to yield improved inhibitory activity against each studied protein receptor.
Keywords: cancer targets; molecular docking; molecular dynamic simulation; pyrazole derivatives.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Targeting EGFR, RSK1, RAF1, PARP2 and LIN28B for several cancer type therapies with newly synthesized pyrazole derivatives via a computational study.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023 Jun;41(9):4194-4218. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2022.2064915. Epub 2022 Apr 20. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023. PMID: 35442150
-
Design, Synthesis, In Vitro Anti-cancer Activity, ADMET Profile and Molecular Docking of Novel Triazolo[3,4-a]phthalazine Derivatives Targeting VEGFR-2 Enzyme.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018;18(8):1184-1196. doi: 10.2174/1871520618666180412123833. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29651967
-
Computational Investigation of 1, 3, 4 Oxadiazole Derivatives as Lead Inhibitors of VEGFR 2 in Comparison with EGFR: Density Functional Theory, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies.Biomolecules. 2022 Nov 1;12(11):1612. doi: 10.3390/biom12111612. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36358960 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Anticancer Fused Pyrazole Derivatives as EGFR and VEGFR-2 Dual TK Inhibitors.Front Chem. 2020 Jan 24;7:917. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00917. eCollection 2019. Front Chem. 2020. PMID: 32039146 Free PMC article.
-
Antineoplastic indole-containing compounds with potential VEGFR inhibitory properties.RSC Adv. 2024 Feb 14;14(9):5690-5728. doi: 10.1039/d3ra08962b. eCollection 2024 Feb 14. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38362086 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preparation, Characterization, and Oral Bioavailability of Solid Dispersions of Cryptosporidium parvum Alternative Oxidase Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 27;25(13):7025. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137025. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000132 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kocyigit U.M., Budak Y., Gürdere M.B., Tekin Ş., Köprülü T.K., Ertürk F., Ceylan M. Synthesis, characterization, anticancer, antimicrobial and carbonic anhydrase inhibition profiles of novel (3aR,4S,7R,7aS)-2-(4-((E)-3-(3-aryl)acryloyl)phenyl)-3a,4,7,7a-tetrahydro-1H-4,7 methanoisoindole-1,3(2H)-dione derivatives. Bioorg Chem. 2017;70:118–125. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2016.12.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dastan T., Kocyigit U.M., Durna Dastan S., Canturk Kilickaya P., Taslimi P., Cevik O., Cetin A. Investigation of acetylcholinesterase and mammalian DNA topoisomerases, carbonic anhydrase inhibition profiles, and cytotoxic activity of novel bis(α-aminoalkyl)phosphinic acid derivatives against human breast cancer. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2017;31:e2171. doi: 10.1002/jbt.21971. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

