Cardamom Extract Alleviates the Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Apoptosis Induced during Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatic Toxicity via Modulating Nrf2/HO-1/NQO-1 Pathway
- PMID: 36354677
- PMCID: PMC9688982
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb44110365
Cardamom Extract Alleviates the Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Apoptosis Induced during Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatic Toxicity via Modulating Nrf2/HO-1/NQO-1 Pathway
Abstract
Acetaminophen (APAP) is the most extensively used and safest analgesic and antipyretic drug worldwide; however, its toxicity is associated with life-threatening acute liver failure. Cardamom (CARD), a sweet, aromatic, commonly used spice, has several pharmacological actions. In the current study, we tried to explore the chemical composition and the hepato-protective effect of ethanolic aqueous extract of CARD to mitigate APAP-induced hepatic toxicity and elucidate its underlying mechanism of action.
Material and methods: Aqueous CARD extract was subjected to LC-TOF-MS analysis to separate and elucidate some of its components. In vivo animal experiments involved five groups of animals. In the normal and cardamom groups, mice were administered either saline or CARD (200 mg/kg), respectively, orally daily for 16 days. In the APAP group, the animals were administered saline orally daily for 15 days, and on the 16th day, animals were administered APAP (300 mg/kg) IP for the induction of acute hepatic failure. In the CARD 200 + APAP group, mice were administered CARD (200 mg/kg) for 15 days, followed by APAP on the 16th day.
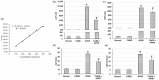
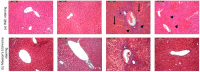
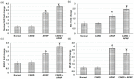
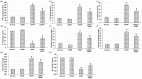
Results: The aqueous extract of CARD showed several compounds, belonging to polyphenol, flavonoids, cinnamic acid derivatives and essential oil components. In the in vivo investigations, APAP-induced impaired liver function, several histopathological alterations, oxidative stress and inflammatory and apoptotic status signified severe hepatic failure. Whereas, pretreatment with the CARD extract prior to APAP administration diminished serum levels of the hepatic function test and augmented Nrf2 nucleoprotein and HO-1 and NQO-1. CARD down-regulated MDA, inflammatory mediators (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α and NF-κB) and apoptotic markers (caspase 3 and 9 and Bax) and amplified the activities of SOD, catalase, GSH-Px and GSH-R in hepatic tissue samples.
Conclusion: CARD extract mitigated the hepatic toxicity induced by APAP. The underlying mechanism of action of such hepato-protective action may be through upregulation of the Nrf2/HO-1/NQO-1 pathway with subsequent alleviation of the oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis induced by APAP. Many of the compounds identified in the CARD extract could be attributed to this pharmacological action of the extract.
Keywords: acetaminophen; cardamom; hepatic function; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Jóźwiak-Bebenista M., Nowak J.Z. Paracetamol: Mechanism of action, applications and safety concern. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2014;71:11–23. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

