Advanced Lung Cancer Patients' Use of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Overall Survival: Real-World Evidence from Quebec, Canada
- PMID: 36354696
- PMCID: PMC9689227
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol29110636
Advanced Lung Cancer Patients' Use of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Overall Survival: Real-World Evidence from Quebec, Canada
Abstract
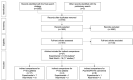
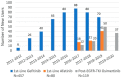
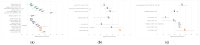
EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) are breakthrough palliative treatments for advanced lung cancer patients with tumors harboring mutations in the EGFR gene. Using healthcare administrative data, three cohorts were created to describe the use of three EGFR-TKIs that are publicly funded in Quebec for specific indications (i.e., 1st-line gefitinib, 1st-line afatinib, and post-EGFR-TKI osimertinib). The main objective was to compare overall survival (OS) among patients receiving these treatments to those in previous experimental and real-world studies. The patients who received EGFR-TKIs for indications of interest between 1 April 2001, and 31 March 2019 (or 31 March 2020, for post-EGFR-TKI osimertinib) were included to estimate the Kaplan-Meier-based median OS for each cohort. An extensive literature search was conducted to include comparable studies. For the gefitinib 1st-line (n = 457), the afatinib 1st-line (n = 80), and the post-EGFR-TKI osimertinib (n = 119) cohorts, we found a median OS (in months) of 18.9 (95%CI: 16.3-21.9), 26.6 (95%CI: 13.7-NE) and 19.9 (95%CI: 17.4-NE), respectively. Out of the 20 studies that we retained from the literature review and where comparisons were feasible, 17 (85%) had similar OS results, which further confirms the value of these breakthrough therapies in real-world clinical practice.
Keywords: advanced cancer; epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs); metastatic cancer; non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); real-word evidence; real-world data; survival; targeted therapies; treatment utilization.
Conflict of interest statement
Among the authors listed above, some were INESSS employees. Their contributions are outlined in the contributions section. INESSS reviewed the article prior to submission for publication. The authors declare no other conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Canadian Cancer Society’s Advisory Committee . Canadian Cancer Statistics: A 2020 Special Report on Lung Cancer. Canadian Cancer Society; Toronto, ON, Canada: 2020.
-
- Canadian Cancer Society’s Advisory Committee in Collaboration with the Canadian Cancer Society, Statistics Canada and the Public Health Agency of Canada . Canadian Cancer Statistics 2021. Canadian Cancer Society; Toronto, ON, Canada: 2021.
-
- Institut National d’Excellence en Santé et en Services Sociaux (INESSS) Création et Caractérisation d’une Cohorte Québécoise de Patients Atteints d’un Cancer du Poumon aà L’aide de Données Clinico-Administratives. Institut National d’Excellence en Santé et en Services Sociaux; Québec, QC, Canada: 2021. p. 152.
-
- Institut National d’Excellence en Santé et en Services Sociaux (INESSS) Groupe d’étude en oncologie du Québec (GEOQ) Algorithmes D’investigation, de Traitement et de Suivi Cancer du Poumon. Institut National d’Excellence en Santé et en Services Sociaux; Québec, QC, Canada: 2014. p. 269.
-
- Institut National d’Excellence en Santé et en Services Sociaux (INESSS) Groupe d’étude en oncologie du Québec (GEOQ) Algorithme: Cancer du Poumon. Institut National d’Excellence en Santé et en Services Sociaux; Québec, QC, Canada: 2020. 2550712501.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

